-
Common NameThiazopyr
-
中文通用名噻唑烟酸
-
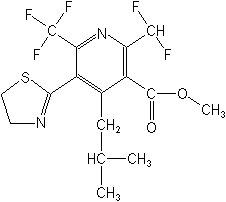
IUPACmethyl 2-difluoromethyl-5-(4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-4-isobutyl-6-trifluoromethylnicotinate
-
CASmethyl 2-(difluoromethyl)-5-(4,5-dihydro-2-thiazolyl)-4-(2-methylpropyl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinecarboxylate
-
CAS No.117718-60-2
-
Molecular FormulaC16H17F5N2O2S
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide
Thiazopyr can be incorporated to a shallow depth in soil prior to planting, or applied as a surface layer after planting. It is most active during germination and seedling development. The product is taken up by the roots and shoots of the plants with little or no translocation from the site of uptake. Higher application rates, sequential or combined treatments with other herbicides (for example oxyfluorfen, diuron or a triazine) are required for adequate control of broadleaf weeds. Thiazopyr has season-long residual activity on grasses. Higher application rates may result in residual activity persisting for longer than twelve months. Product applied preplant remains in the soil until activated by irrigation or rainfall. Granular formulations have formerly been used in no-till systems to avoid loss of sprayed product on foliage or "trash".
In alfalfa field trials, thiazopyr gave better or equal control of Cuscuta epithymum at lower application rates than standard. In turfgrass, it gave better control of Cyperus spp than imazaquin. Thiazopyr is safe to target crops when used pre-plant. Some transient phytotoxicity has been noted in alfalfa. An application of 506 g/ha controlled broadleaf weeds in strawberries in Oregon all summer, with no phytotoxicity or yield reductions.
Monsanto published early results of experiments to genetically modify tomato plants to be resistant to thiazopyr (Pesticide Biochem Physiol, 1998). -
CropUseCropUses:
citrus, cotton, peanuts, fruit (including vines and pineapples), vegetables, alfalfa, soybeans, maize, rice, plantation crops (including sugar cane), nuts (non-bearing), forestry, noncrop use, sugar cane, vines (non-bearing)
Cotton
100-560 g ai/ha
Alfalfa
280-1,120 g ai/ha
Citrus
560-1, 120 g ai/ha
Peanuts
140-450 g ai/ha
Trees/vines
250-1, 220 g ai/ha
Sugar cane
120-480 g ai/ha
No-till/reduced-till soybeans
: 224-448 g ai/ha
-
Premix
Type
AI concn
Emulsifiable concentrate (EC)
24% (w/v)
Granule (GR)
5% (w/w)
Water-dispersible granule (WG)
50% (w/w)
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:396.4; Physical form:Light tan, crystalline solid, with a sulfur odour. Density:1.373 (25 °C); Composition:Tech. is 93%. Melting point:77.3-79.1 °C; Vapour pressure:0.27 mPa (25 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.89 (21 °C); Solubility:In water 2.5 mg/l (20 °C). In methanol 28.7, hexane 3.06 (both in g/100 ml, 20 °C); Stability:Aqueous photolysis DT50 15 d.;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to eyes; practically non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.2 mg/l air.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae: EC50 for Selenastrum 0.04, Anabaena 2.6, Skeletonema 0.094 mg/l.Bees: LD50 >100 µg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1913 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 6.1 mg/l.Fish:LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 3.4, rainbow trout 3.2, sheepshead minnow 2.9 mg/l. Lifecycle NOEC for fathead minnow 0.092 g/l.Worms:LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg soil.Other aquatic spp.: EC50 for Eastern oyster 0.82, mysid shrimp 2.0 mg/l. IC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 0.035 mg/l.Other beneficial spp.:In laboratory studies, harmless to spiders, slightly harmful to predatory mites and beetles, moderately harmful to parasitic wasps.
Environmental fate:
Animals:Rapidly and extensively metabolised and eliminated. Oxidised by rat liver microsomes via sulfur and carbon oxidations and via oxidative de-esterification. Bioconcentration factor in bluegill sunfish 220; rapidly eliminated, with 98% elimination within 14 Soil:In soil, degraded by both soil micro-organisms and hydrolysis. Soil dissipation studies across multiple locations in the US indicate average DT50 64 d (8-150 d). Vertical mobility was found to be minimal, with few detections belPlant:Studies in several species indicate thiazopyr is initially metabolised in the dihydrothiazole ring by plant oxygenases to the sulfoxide, sulfone, hydroxy derivative and thiazole, and is also de-esterified to the carboxylic acid;
Mallard duck
LC50 >5,620 ppm
Bluegill sunfish
LC50 3.4 mg/litre
Trout
LC50 3.2 mg/litre
Daphnia
LC50 5.9 mg/litre
Bee
LD50 >100 μg/bee
Fate in soil:
Thiazopyr is degraded primarily by soil microbes and secondarily via soil hydrolysis. The half-life in soil ranges from 8 to 150 days. Mobility in soil is minimal.Fate in aquatic systems:
The risk of bioaccumulation is reported to be low.Fate in other:
Thiazopyr is stable to UV light under dry conditions. -
Transport InformationHazard Class:O (Obsolete as pesticide, not classified)
Porduct NewsMore
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide
Colombia’s Constitutional Court bans chlorpyrifos
ADAMA Canada moves forward with lambda-cyhalothrin sales for 2023
Mexico: Import of glyphosate drops from 16,500 tons to 8,200 tons
Glyphosate prices drop 30% in Argentina
One year extension of EU glyphosate approval failed to pass in the latest meeting
Palmer amaranth in two southern U.S. states now resistant to S-metolachlor

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe