-
Common NameLufenuron
-
中文通用名虱螨脲
-
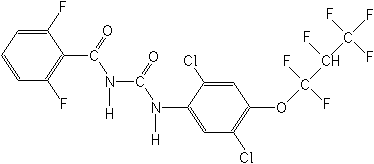
IUPAC(RS)-1-[2,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoropropoxy)phenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
-
CASN-[[[2,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoropropoxy)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
-
CAS No.103055-07-8
-
Molecular FormulaC17H8Cl2F8N2O3
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityInsecticide/acaricide/Miticide
Lufenuron is only active against immature larval and nymphal stages of arthropods. The product is primarily active following ingestion. It has no knockdown activity. After ingestion, feeding ceases and death follows within a few days. It is a potent ovicide on Cydia and Lobesia spp and some trans-ovarian activity has also been observed. Optimum control of fruit pests is obtained when lufenuron is applied at egg hatching. The product is not plant-systemic but has some translaminar activity against Spodoptera littoralis on cotton leaves. Leaf-feeding caterpillars are controlled in all instars. On vines, the product's residual activity means that in many cases only one application per season is required.
The formulated product, Match, is safe to all plant varieties tested. In field trials, lufenuron gave equal or better results than standard insecticides. The company has demonstrated that the fermentation or the quality of wines made from lufenuron-treated grapes is not affected by the product. It is safe to adults of beneficial insects and the company recommends its use in IPM programmes.
Lufenuron has been shown (BCPC 2000) to exert little effect on the egg hatching of the American bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera) but provided good control of the first instar stage. -
CropUseCropUses:
apples, aubergines, Brussels sprouts, cabbages, Chinese cabbages, cotton, grapefruits, Japanese pears, Japanese radishes, leeks, lemons, limes, loquats, maize, onions, oranges, ornamentals, pears, pimentos, potatoes, quince, soybeans, sugar beets, tea, tomatoes, vines, yams
Maize
12.5-100 g ai/ha
Vegetables
15-30 g ai/ha
Fruit
50 g ai/ha
Cotton
20-50 g ai/ha
Potatoes
40 g ai/ha
-
PremixProfenofos+Lufenuron
Lufenuron+Emamectin benzoate
Lufenuron+Chlorfenapyr
Lambda-cyhalothrin+Lufenuron
Diafenthiuron+Lufenuron
Bifenthrin+Lufenuron
Emulsifiable concentrate.
Premix Parters: beta-cypermethrin; naled;
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:511.2; Physical form:Colourless crystals. Density:1.66 at 20℃ ( OECD 109); Composition:Tech. is >98%. Melting point:168.7-169.4 ℃ ( OECD 102); Vapour pressure:<4 ×10-3 mPa (25 ℃) ( OECD 104); Henry constant:<3.41 × 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 ( calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 5.12 (25 ℃) ( OECD 117); pKa:>8.0; Solubility:In water <0.06 mg/l (25 ℃). In ethanol 41, acetone 460, toluene 72, n-hexane 0.13, n-octanol 8.9 (all in g/l, 25 ℃).; Stability:Stable in air and light. In water, DT50 32 d ( pH 9), 70 d ( pH 7), 160 d ( pH 5).
-
Toxicology
Oral:Acute oral LD50for rats >2000 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h, 20℃
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae:Slightly toxic to algae.Bees: LC50 (oral) >197 μg/bee. LD50 (topical) >200 μg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5200 mg/ kg.Daphnia:Toxic to Daphnia.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >73, carp >63, bluegill sunfish >29, catfish >45 mg/l.Worms:No adverse effects on earthworms.
Environmental fate:
Animals:Major route of elimination was via faeces, with very little degradation.Soil:Lufenuron was rapidly degraded in biologically active soils under aerobic conditions. DT50 13-20 d. Lufenuron showed a very strong adsorption onto soil particles: Koc (mean value) 38 mg Plant:No metabolites occurred in significant amounts in the investigated target crops (cotton, tomatoes).
Fate in soil:
Lufenuron is broken down by soil microbes, it has a soil half-life of two weeks under normal conditions. It is strongly adsorbed by soil particles. The potential for contamination of groundwater is low.Fate in aquatic systems:
Lufenuron is degraded by photolysis and hydrolysis. The photolytic half-life is 85 days. The rate of hydrolysis is dependent on temperature and pH, being fastest at high temperatures and pH.Transport InformationHazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Sumitomo Chemical launches insecticide Abaday for caterpillar control in Brazil
Related CompaniesMore
Shanghai Heben-Eastsun Medicaments Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Thiamethoxam Azoxystrobin Boscalid Chlorfenapyr Difenoconazole Fludioxonil Indoxacarb Picoxystrobin Pyraclostrobin Tebuconazole
Xuzhou Jinhe Chemical Co.,Ltd.
Country: China
Thiabendazole Metaldehyde Niclosamide Olamine Tricyclazole Brassinolide Chlorfenapyr Quizalofop-p-ethyl Cyhalofop-butyl LUFENURON Paraquat Dichloride
SINO AGRO-CHEMICAL INDUSTRY LTD.
Country: China
Prothioconazole Azoxystrobin Pyraclostrobin Methoxyfenozide Bifenazate Bispyribac-sodium Nicosulfuron Tebuconazole Pyribenzoxim Penoxsulam
Country: China
Picloram Glyphosate 2,4-D Paraquat Lufenuron Chlorpyrifos Chlorothalonil Imidacloprid Cymoxanil Metalaxyl+Cuprous Oxide
Shenzhen Baocheng Chemical Industry CO.,LTD.
Country: China
Glyphosate Emamectin benzoate Lambda-cyhalothrin Pyraclostrobin Bromacil Glufosinate-ammonium Tembotrione Prothioconazole Topramezone Chlorantraniliprole

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe