-
Common NameAzafenidin
-
中文通用名唑啶草酮
-
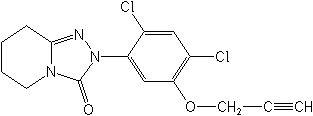
IUPAC2-(2,4-dichloro-5-prop-2-ynyloxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridin-3(2H)-one
-
CAS2-[2,4-dichloro-5-(2-propynyloxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridin-3(2H)-one
-
CAS No.68049-83-2
-
Molecular FormulaC15H13Cl2N3O2
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityAzafenidin is a broad spectrum herbicide for application to the ground beneath perennial crops prior to weed emergence. It controls annual and perennial weeds. Azafenidin is taken up by the roots and shoots of weeds. The herbicide is only slightly mobile in the phloem and xylem, resulting in weak post-emergence activity. Azafenidin controls weeds for up to 3 months, depending on species. Annual weeds may require up to two additional post-emergence applications of azafenidin alone or tank mixed with contact or post-emergence herbicides. Speedwell is exceptionally tolerant to azafenidin. The product can be applied post-emergence. It controls weeds resistant to triazine, cyclohexanedione and aryloxy-phenoxypropionate herbicides and those resistant to ALS inhibitors.
Azafenidin is not absorbed by the roots of crops and is safe to target crops at up to three times the recommended use rate. The herbicide is not recommended for use in vineyards of less than two years old, but otherwise can be used at any growth stage of the crop. Selectivity in vines is largely positional, associated with the low mobility of the product and the deep roots of the crop.
Studies in commercial pineapple growing situations showed that azafenidin applied pre-planting could provide effective control of perennial grasses and annual weeds at a dose rate considerably lower than the current reference, bromacil. Bromacil registrations are under threat due to concerns over detection of the herbicide in groundwater. The studies also showed that azafenidin applied at 0.7 kg/ha could suppress growth of purple nutsedge (Cyperus rotundus).
Early season applications of azafenidin to hardwood seedlings of sweetgum, sycamore and cottonwood in the US indicated that crop tolerance was good and greater than that for oxyfluorfen or sulfometuron. Field trials in Brazil showed that azafenidin applied at rates of 300-800 g/ha produced phytotoxic symptoms in Eucalyptus canadensis.
In trials conducted over 3 years in France on ornamental trees and shrubs, azafenidin applied pre-emergence at 480 g ai/ha provided broad spectrum control of annual grasses and broadleaf weeds plus an inhibitory effect on the growth of the liverwort, Marchantia polymorpha. Good residual control was achieved over a period of 4-6 months. No phytotoxicity was observed on the species tested.
Field trials conducted over two years in the US demonstrated that azafenidin, applied at 420-840 g ai/ha to sugar cane, provided good control (87-100%) of red morningglory (Ipomoea coccinea). Control was superior to the commercial references (atrazine, diuron, terbacil, metribuzin). The applications were made underneath the crop canopy in May to June and followed a layby cultivation. Slight discolouration was observed on the sugarcane foliage but the plants recovered rapidly. -
CropUseCrop uses:
citrus, forestry, nuts, olives, ornamentals, pineapples, pome fruits, stone fruits, sugar cane, vines
Vines
citrus: 240 g ai/ha (up to two applications per season)
Olives
240 g ai/ha
Ornamental trees and shrubs
480 g ai/ha
-
Premix
Type
AI concn
ranule (GR)
0.3% (w/w)
Water-dispersable granule (WG)
80% (w/w)
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight: 338.2 g/mol
-
Toxicology
Acute oral: LD50 >5,000 mg/kg.
-
Environmental Profile
Daphnia magna[48 h]
LC50 38 mg/L
Bobwhite quail
LD50 >2,250 mg/kg
Bee oral [48 h]
LD50 >20 μg/bee
Bee contact [48 h]
LD50 >100 μg/bee
Sheepshead minnow [96 h]
LC50 >25 mg/L
Mallard duck
LD50 >2,250 mg/kg
Rainbow trout [96 h]
LC50 33 mg/L
Bluegill sunfish [96 h]
LC50 48 mg/L
Fate in soil:
Azafenidin binds tightly to soil particles and shows minimal movement in leaching experiments; hence it is not expected to leach to groundwater. It is degraded primarily by microbes and photolysis in soil and has a half-life of 4 - 129 days. The Koc is 186 - 579 depending on soil type, soil pH.Fate in aquatic systems:
Azafenidin is stable to hydrolysis but is degraded microbially and by photolysis in aquatic systems. The half-life is 96 days under laboratory conditions.
DuPont carried out a prospective groundwater monitoring study on a highly vulnerable site. Results have been reported to the US EPA.
Porduct NewsMore
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide
Colombia’s Constitutional Court bans chlorpyrifos
ADAMA Canada moves forward with lambda-cyhalothrin sales for 2023
Mexico: Import of glyphosate drops from 16,500 tons to 8,200 tons
Glyphosate prices drop 30% in Argentina
One year extension of EU glyphosate approval failed to pass in the latest meeting
Palmer amaranth in two southern U.S. states now resistant to S-metolachlor

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe