-
Common NameDichlobenil
-
中文通用名敌草腈
-
IUPAC2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile
-
CAS2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile
-
CAS No.1194-65-6
-
Molecular FormulaC7H3Cl2N
-
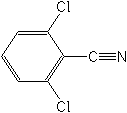
Molecular Structure
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:172.0. Physical form:Colourless crystals, with an aromatic odour ( tech., off-white crystals). Composition:Tech. grade dichlobenil is 98% pure. Melting point:145-146 °C ( tech., 143.8-144.3 °C); Vapour pressure:88 mPa (20 °C) (gas saturation method); Henry constant:1.10 Pa m3 mol-1 ( calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 2.70; Solubility:In water 14.6 mg/l (20 °C). In acetone, dioxane, benzene 50 (all in g/l, 8 °C). In dichloromethane 100 g/l (20 °C). In xylene 53, ethanol 15, cyclohexane 3.7 (all in g/l, 25 °C). Very slightly soluble in non-polar solvents (<10 g/l). Stability:Stable to heat, <270 °C. Stable to acids, but rapidly hydrolysed by strong alkalis to 2,6-dichlorobenzamide. Photolytic DT50 in water 10.2 d (natural sunlight at 40 Northern latitude). Stable to heat, acids; hydrolyzed by alkali to the benzamide. Slightly soluble in most organic solvents.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral
LD50 for rats 4460, male mice 1014, female mice 1621 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for albino rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin or eyes (rabbits). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >250 mg/m3. Phytotoxicity:Some conifers are susceptible to dichlobenil vapour, due to their bark structure. -
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae:50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 2.0, Anabaena flos-aquae 2.7 mg/l.Bees:Not toxic to bees; LD50 (contact) >11 µg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 683 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail c. 5200, mallard ducks >5200 mg/ kg diet.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 6.2 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) 5-13 mg/l (various fish species).Worms: LD50 for earthworms >1000 mg/ kg substrate.Other beneficial spp.:Harmless to carabids. No effect on soil microflora.
Environmental fate:
Animals:Metabolised and excreted mainly as hydroxylated conjugates. For fate in animals, see K. I. Beynon & A. N. Wright, Residue Rev., 1972, 43, 23; A. Verloop, ibid., 1972, 43, 55.Soil:Has a low leaching potential. In soil, dichlobenil gradually undergoes microbial degradation to 2,6-dichlorobenzamide, which is slowly broken down to 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid. Half-life of dichlobenil in soil may vary between 1 and 6 months, depending on Plant:The soil metabolite 2,6-dichlorobenzamide can be taken up by plants via the roots. Plant metabolism involves ring hydroxylation (at the 3-position and, to a lesser extent, at the 4-position) of both dichlobenil and 2,6-dichlorobenzamide.
WATER SOLUBILITY: 21 mg/l at 25°C -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III (Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe