-
Common NameDichlorprop
-
中文通用名2,4-滴丙酸
-
IUPAC(RS)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propionic acid
-
CAS2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid
-
CAS No.120-36-5
-
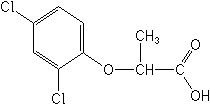
Molecular FormulaC9H8Cl2O3
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide
-
PremixMCPA+dichlorprop-P+mecoprop-P
Dichlorprop-P-2-ethylhexyl+2,4-d 2-ethylhexyl ester
Invert emulsion of butoxyethanol, ester, aqueous solution of (potassium or amine salt), and emulsifiable concentrate of isooctyl and butoxyethanol esters (600-720 g/l), soluble concentrates (600-720 g/l). Premix Parters: chlorpyrifos; cypermethrin; diazinon; phosalone.
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:235.1. Physical form: Colourless crystals; ( is a brown powder with a phenolic odour). Density:1.42. Composition:Commercial dichlorprop is a racemate, only the (+)-isomer () being herbicidally active. Melting point:116-117.5 °C; ( tech., 114 °C); Flash point:204 °C (open cup); Vapour pressure:<1×10-2 mPa (20 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 1.77 (unstated pH); pKa:3.00. Solubility:In water 350 mg/l (20 °C). In acetone 595, isopropanol 510, benzene 85, toluene 69, xylene 51, kerosene 2.1 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Sodium salt: In water 660 g acid equivalent/l (20 °C). Diethanolamine salt: In water 740 g acid equivalent/l. Stability:The acid is very stable, and forms sparingly-soluble, slightly-active salts with heavy metals. Solubility at room temperature in xylene 4.9%; toluene 6.2%; ethanol 153%; heptane 0.5% w/v.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral
LD50 for rats 825-1470 mg/kg, mice 400 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >4000 mg/kg, mice 1400 mg/kg. Eye and skin irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.65 mg/l air. -
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae:ErC50 for fresh-water green algae 1100 mg/l.Bees:Not toxic to bees. Birds: LD50 for Japanese quail 504 mg/kg.Daphnia: LOEC (survival) 100 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 521 mg/l; 165 mg/l (48 h) (bluegill); Isooctyl ester: 16 mg/l; Butoxyethanol ester: 1.1 mg/l (bluegill); 100-220 mg/l (96 h) (trout). Worms:(14 d) c. 1000 mg/kg dry soil.
Environmental fate:
Animals:Metabolism studies suggest that dichlorprop is absorbed and excreted essentially unchanged.Soil:In soil, metabolism involves degradation of the side-chain to 2,4-dichlorophenol, ring hydroxylation, and ring opening;DT50 21-25 d. Koc c. 12-40. Due to the high rate of metabolic breakdownPlant:In plants, dichlorprop is metabolised in a similar manner to that in soil. For details of metabolites identified in barley, see G. Baerenwald et al., Z. Naturforsch. C: Biosci., 1987, 42(4), 486.
WATER SOLUBILITY: Room temperature 825 ppm. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:WARNING; Hazard Class:II (Moderately hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe