-
Common NameFipronil
-
中文通用名氟虫腈
-
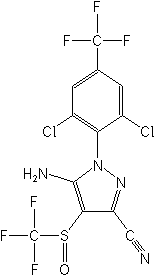
IUPAC5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-p-tolyl)-4-trifluoromethylsulfinylpyrazole-3-carbonitrile
-
CAS5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl]-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
-
CAS No.120068-37-3
-
Molecular FormulaC12H4Cl2F6N4OS
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityFipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide active by contact and ingestion, which is effective against adult and larval stages. It disrupts the insect central nervous system by interfering with the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) - regulated chlorine channel. It is systemic in plants and can be applied in a variety of ways. Fipronil can be used at the time of planting to control soil pests. It can be applied in-furrow or as a narrow band. It requires thorough incorporation into the soil. Granular formulations of the product can be used in broadcast applications to paddy rice. As a foliar treatment, fipronil has both preventative and curative activity. The product is also suitable for use as a seed treatment.
Vil-Nil is a compost-incorporated granule formulation for the control of vine weevils in ornamental plants. This formulation binds to plant roots and acts as a preventative treatment. It persists in the soil for at least two seasons. Fipronil has also been developed for use in baits for the control of grasshoppers, cockroaches and ants.
In field trials, fipronil showed no phytotoxicity at the recommended rates. It controls organophosphate-, carbamate- and pyrethroid-resistant species and is suitable for use in IPM systems. Fipronil does not adversely interact with ALS-inhibiting herbicides.
Bayer CropScience voluntarily withdrew registrations of certain pesticide products that contain fipronil for use on rice or rice seed. The cancellation was effective from the 1st of July 2004.
Two reports in J. Econ. Entomol. (2003) summarise the toxicity of fipronil against the Formosan subterranean termite, Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki, which is an economically important pest in the US. Acute toxicity from topical applications was greater in workers than soldiers. Later assessments showed little difference on the two groups, with an LD50 at 72h of < 2.0 ng/insect. Treated soldiers placed near untreated workers resulted in higher mortality of the workers, but the reverse process (from treated workers to untreated soldiers) did not result in significant horizontal transmission. Fipronil rates of up to 0.063% showed no repellency, whereas the higher rate of 0.125% was repellent to workers. -
CropUseCropUses:
alfalfa, aubergines, bananas, beans, brassicas, cabbages, cauliflowers, chillies, crucifers, cucurbits, citrus, coffee, cotton, crucifers, garlic, maize, mangos, mangosteens, melons, oilseed rape, onions, ornamentals, peas, peanuts, potatoes, rangeland, rice, soybeans, sugar beet, sugar cane, sunflowers, sweet potatoes, tobacco, tomatoes, turf, watermelons
Maize: 200 g ai/ha; 2, 500 g ai/tonne seed
Sugar beet: 200 g ai/ha
Sunflowers: 200 g ai/ha; 5, 000 g ai/tonne seed
-
PremixProbenazole+fipronil
Imidacloprid+fipronil
Fipronil+deltamethrin
Fipronil+Chlorpyrifos
Acephate+Fipronil
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:437.2; Physical form:White solid. Density:1.477-1.626 (20 °C); Melting point:200-201 °C; ( tech., 195.5-203 °C); Vapour pressure:3.7 ×10-4 mPa (25 °C); Henry constant:3.7 ×10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 ( calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 4.0 (shake flask method); Solubility:In water 1.9 ( pH 5), 2.4 ( pH 9), 1.9 (distilled) (all in mg/l, 20 °C). In acetone 545.9, dichloromethane 22.3, hexane 0.028, toluene 3.0 (all in g/l, 20 °C).; Stability:Stable in water at pH 5 and 7; slowly hydrolysed at pH 9 ( DT50 c. 28 d). Stable to heat. Slowly degrades in sunlight (c. 3% loss after 12 d continuous irradiation); rapidly pho;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats 97, mice 95 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000, rabbits 354 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant ( OECD criteria). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.682 mg/l ( tech.; nose only exposure).
-
Environmental Profile
Ecotoxicology:
Algae: EC50 (96 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.068 mg/l; (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >0.16, Anabaena flos-aquae >0.17 mg/l.Bees:Highly toxic to honeybees, both by direct contact and by ingestion. However, no risk to bees when used as a soil or seed treatment.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 11.3, mallard ducks >2000, pheasants 31, red-legged partridges 34, house sparrows 1120, pigeons >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 0.19 mg/l; for D. carinata (48 h) 3.8 mg/l.Fish:Acute LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 85, rainbow trout 248, European carp 430 mg/l.Worms:Non-toxic.
Environmental fate:
Fate in soil:
In laboratory studies, fipronil has a half-life of 122-128 days in oxygenated sandy loam soil. In field studies, half-life on soil surfaces ranges from 0.7 to 1.7 months, whilst for soil incorporation it is 3 to 7.3 months. Fipronil has low soil mobility; it binds to the soil and the residues remain in the upper 12 inches of soil. The average Koc value is 803. There is little potential for groundwater contamination.
Aerobic soil metabolism studies give the half-life of fipronil in sandy loam to be 122 days.
In anaerobic systems, fipronil degrades slowly in water and sediment with a half-life of 116-130 days. In an aerobic metabolism study, fipronil readily partitioned from the aqueous layer into the sediment.
In a field dissipation study in Niger, 25% of the original applied dose of fipronil (8 g ai/ha) was recovered after 3 days. Four degradates were also identified including a sulfide due to reduction in soil, an amide from hydrolysis, and a sulfone from oxidation in soil. A desulfinyl photodegradate was also identified.
Thus in soil, fipronil dissipates by soil binding along with gradual microbial breakdown.Fate in aquatic systems:
Fipronil is stable to hydrolysis at 22°C at pH 9.1 (DT50 1100 days) and pH 7.1 (DT50 1100 days), whereas at 32°C, the half-life is 11.3 days at pH 9.1 and 15.6 days at pH 7.1.
Fipronil undergoes photodegradation in water with a half-life of 3.6 hours. Thus photolysis is a more important pathway for degradation of aqueous fipronil.
Ground water concentrations of fipronil calculated using the SCI-GRO model (shallow groundwater on highly vulnerable US sites) were 0.055 ppb for maize and 0.00804 ppb for rice. Based on environmental fate assessment, fipronil has the potential to move into surface waters. However, when fipronil is used as an in-furrow application, the run-off potential of fipronil residues is expected to be lower than for unincorporated surface application techniques. The maximum fipronil surface water concentrations for acute and chronic exposure based on GENEEC surface water modelling were found to be for corn, acute 2.05 ppb, chronic 0.78 ppb; for rice, acute 1.45 ppb, chronic 0.40 ppb. These values are less than the drinking water lowest levels of concern of 810 ppb and 220 ppb in surface and ground water for acute risk, and 6.67 ppb and 1.77 ppb for chronic risk. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:WARNING; Hazard Class:II(Moderately hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Vietnam bans chlorpyrifos-ethyl and fipronil products
Study suggests fipronil caused massive honeybee die-off in France
AllierBrasil registered MARATHON 800 WG in Brazil
Millions of eggs contaminated by fipronil removed from European shelves
Helm gets registration for Comboio 80 WG insecticide
Nufarm launches insecticide Maestro for seed treatment in Brazil
UPL launches insecticide seed treatment product Start in Brazil
Bayer launches Poncho Energy technology for seed protection in Brazil
EFSA to review fipronil data collected for risk assessment for bees
EFSA calls for data related to risk to bees from fipronil
Related CompaniesMore
SINO CHEMTECH (SHANGHAI) CO., LTD
Country: China
Tribenuron-methyl Nicosulfuron Dimethomorph Clodinafop-propargyl Diazinon Emamectin benzoate Imidacloprid Thiamethoxam Chlorpyrifos+cypermethrin Bromoxynil octanoate+MCPA-isooctyl BAAPE IR3535
Anhui Fengle Agrochemical Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Tribenuron-methyl Dimethomorph Bentazone Carboxin Quizalofop-P-ethyl Nicosulfuron Clomazone Propiconazole Chlorpyrifos Clopyralid Clodinafop-propargyl
Jiangsu Subin Agrochemical Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Thiamethoxam Pymetrozine Fludioxonil Dinotefuran Lufenuron+Emamectin benzoate Emamectin benzoate Azoxystrobin+cyproconazole Teflubenzuron Thiamethoxam+lambda-cyhalothrin
SML Limited (Formerly known as Sulphur Mills Limited)
Country: India
Sulphur Imidacloprid Lambda-cyhalothrin Thiamethoxam+lambda-cyhalothrin Thiamethoxam Fipronil Tebuconazole Tebuconazole+Sulphur Clomazone Chlorpyrifos
SINO AGRO-CHEMICAL INDUSTRY LTD.
Country: China
Prothioconazole Azoxystrobin Pyraclostrobin Methoxyfenozide Bifenazate Bispyribac-sodium Nicosulfuron Tebuconazole Pyribenzoxim Penoxsulam

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe