-
Common NameSiduron
-
中文通用名环草隆
-
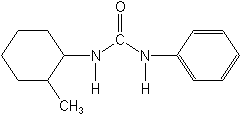
IUPAC1-(2-methylcyclohexyl)-3-phenylurea
-
CASN-(2-methylcyclohexyl)-N′-phenylurea
-
CAS No.1982-49-6
-
Molecular FormulaC14H20N2O
-
Molecular Structure
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:232.3; Physical form:Colourless crystals. Density:1.08 (25 °C); Composition:Tech. is >98%. Melting point:133-138 °C; Vapour pressure:5.3 × 10-4 mPa (25 °C); Henry constant:6.8 × 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 ( calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.8; Solubility:In water 18 mg/l (25 °C). In dimethylacetamide 367, dimethylformamide 260, ethanol 160, isophorone, dichloromethane 118 (all in g/kg, 25 °C).; Stability:Stable up to its melting point and in neutral aqueous solutions. Decomposes slowly in acid and alkaline media. DT50 >>30 d (pH 5, 7, 9, 25 °C).;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats >7500 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5500 mg/kg (maximum feasible dose). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.8 mg/l. Phytotoxicity:Bermuda grass and certain bent grasses may be injured when applied pre-emergence. ADI:(Japan) 0.14 mg/kg.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae: EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 250mg/l.Birds:Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducklings and bobwhite quail >10 000 mg/kg diet.Daphnia: EC50 (48 h) 18 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 14, bluegill sunfish 16 mg/l.
Environmental fate:
Soil:In soil, resists leaching. Microbial degradation occurs, DT50 c. 120-150 d; metabolites include methylcyclohexylurea, methylcyclohexylamine, phenylurea and aniline. In water, photolysis DT50 2Plant:In studies with 14C-labelled siduron, no metabolites were detected in barley plants after an 8-day absorption period. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe