-
Common NameSpiroxamine
-
中文通用名螺环菌胺
-
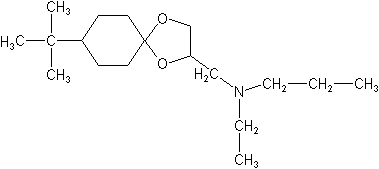
IUPAC8-tert-butyl-1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-2-ylmethyl(ethyl)(propyl)amine
-
CAS8-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N-ethyl-N-propyl-1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-2-methanamine
-
CAS No.118134-30-8
-
Molecular FormulaC18H35NO2
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityFungicide
Spiroxamine is particularly effective in the control of Erysiphe graminis on wheat and barley. The product blocks fungal sterol biosynthesis by inhibition of delta14 reductase, as opposed to the azole fungicides which act by blocking C14 demethylation. It acts preventatively by blocking the formation of the appressoria. When used as a curative treatment, the haustoria formed in the plant tissues are distorted. The product also destroys mycelia and conidia present on the surface of the plant. Spiroxamine penetrates the leaf and is translocated acropetally to the leaf tip. Bayer reports that the product shows even distribution throughout the leaf and does not accumulate in the leaf tip.
In field trials, the product has shown comparable activity to DMI's, morpholines, sulfur and piperidines. In cereals, the lower application rate is particularly suitable for higher growth stages; higher rates are required for good persistance of activity. In vines, Prosper and Hoggar should be applied at 14-day intervals, but not more than three times a season. The product has been shown not to affect either the fermentation or the organoleptic qualities of wines. On hops, a maximum of two applications can be made per season, at 28 day intervals, and at least 28 days pre-harvest.
Bayer states that no cross-resistance has been observed with strobilurins, quinolines, triazoles and piperidines. The company recommends its use in resistance management programmes. -
CropUseCropUses:
barley, hops, oats, rye, vines, wheat
Cereals
500-800 g ai/ha
Vines
300-400 g ai/ha
Hops
18 oz/acre Accrue (1.3 l./ha)
-
PremixSpiroxamine+Tebuconazole
Emulsifiable concentrate, emulsion, oil in water. Premix Parters: chlorsulfuron sulfometuron-methyl; cloransulam-methyl; 2,4-D dicamba mecoprop-P; 2,4-D dicamba quinclorac; metribuzin;
Type
AI concn
Emulsifiable concentrate (EC)
50% (w/v)
80% (w/v)
Capsule Suspension (CS)
30.9% (w/v)
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:297.5; Physical form:Faintly yellowish liquid; ( tech. is a light brown, oily liquid). Density:A and B both 0.930 (20 °C); Composition:Comprises 2 diastereoisomers, A and B, in the proportions 49-56% and 51-44%, respectively. Melting point:<-170 °C (separate diastereoisomers, spiroxamine A, spiroxamine B, and tech. mixture of both diastereoisomers); Flash point:147 °C; Vapour pressure:A: 9.7 mPa (20 °C); B: 17 mPa (25 °C) (both extrapolated); Henry constant:A: 2.5 × 10-3; B: 5.0 × 10-3 (both in Pa m3 mol-1, 20 °C, calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):A: logP = 2.79; B: logP = 2.92 (unstated pH); pKa:6.9, base; Solubility:In water, mixture of A and B: >200 × 103 mg/l (pH 3, 20 °C); A: 470 ( pH 7), 14 ( pH 9); B: 340 ( pH 7), 10 ( pH 9) (both diastereoisome; Stability:Stable to hydrolysis and photodegradation; provisional photolytic DT50 50.5 d (25 °C).;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male rats c. 595, female rats 500-560 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats >1600, female rats c. 1068 mg/kg b.w. Severe skin irritant; not an eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for male rats c. 2772, female rats c. 1982 mg/m3. ADI:(US) 0.027 mg/kg b.w.; (Japan, Australia) 0.024 mg/kg b.w.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
?Algae:ErC50 (96 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.012, Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata 0.0194 mg/l.Bees:No risk to bees.Birds: LD50 565 mg/kg.Fish: LD50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 18.5 mg/l.Worms: LC50 ×1000 mg/kg dry wt. substrate.?
Environmental fate:?
Animals:Biokinetics and metabolism studies in rats showed a high degree of absorption of radioactivity followed by fast elimination from the body (>97 % within 48 h after oral administration). The radioactivity was readily distributed from the plSoil:Readily degraded in soil, ultimately to CO2; oxidation on the t-butyl moiety and des-alkylation of the amine are the primary reaction steps. The des-alkylated compounds were either further oxidised to the corresponding acids or furtherPlant:Extensively metabolised in spring wheat and grapes, by oxidation, desalkylation and cleavage of the ketal structure; the resulting metabolites bearing a hydroxylated t-butyl group or an aminodiol were further conjugated. In the confined rotationa
Bobwhite quail
LD50 565 mg/kg
Rainbow trout
LC5011.5 mg/L
Earthworms
LC50 31,000mg/kg dry soil
Daphnia magna
EC50 5.1 mg ai/L
Green algae
EC50 0.0032 mg ai/L
Fate in soil:
The soil half-life of spiroxamine ranges from 35-64 days.Fate in aquatic systems:
The half-life in supernatant water is between 12 and 13 hours. -
Transport InformationHazard Class:II(Moderately hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
ECHA adopted opinions on CLHs for three pesticides
Spiroxamine Cyproconazole momfluorothrin
Related CompaniesMore
Country: China
Glufosinate-ammonium 2,4-D MCPA Dicamba Propanil Clethodim Glyphosate Captan Flumioxazin Sulfentrazone
Country: China
ABAMECTIN CARBOFURAN Chlorpyrifos LAMBDA-CYHALOTHRIN 2,4-D GLYPHOSATE ALUMINIUM PHOSPHIDE EDDHA-Fe 6% ZINC SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE
Country: China
2,4-D 2-ETHYLHEXYL ESTER florasulam+2,4-d 2-ethylhexyl ester Difenoconazole+Propiconazole Diflufenican+isoproturon Cymoxanil+famoxadone Fludioxonil+cyprodinil Flufenacet+diflufenican Glyphosate+2,4-D Imazamox+Bentazone Spiroxamine+Tebuconazole
Shaanxi Hengrun Linong Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Country: China

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe