-
Common NameSulfosulfuron
-
中文通用名磺酰磺隆
-
IUPAC1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-(2-ethylsulfonylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-ylsulfonyl)urea
-
CASN-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-2-(ethylsulfonyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-sulfonamide
-
CAS No.141776-32-1
-
Molecular FormulaC16H18N6O7S2
-
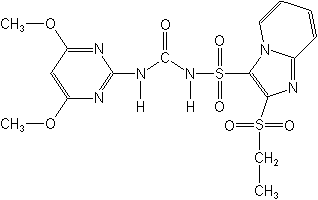
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide
Sulfosulfuron is a post-emergence herbicide primarily for wheat. It controls annual and perennial grasses and a number of broadleaf weeds including cleavers (Galium aparine). Following application there is an immediate cessation of growth and darkening of green tissue followed by a reddening of the stem base. Necrosis of the leaves and stems ensues, and weeds die within 40 days of application, depending on the rate of plant growth. Monsanto recommends the use of surfactants to optimise the herbicide's activity. Sulfosulfuron controls Alopecurus repens and Bromus species not currently controlled by wheat herbicides. The activity against ripgut brome (Bromus rigidus) and foxtail brome (Bromus rubens) was reported in Weed Technology (2001).
The product has been shown to damage barley, oat, sorghum, sugar beet and sunflower crops (see Weed Technology, 2001 for a report of the effects of MON 37500 residues on sorghum and sunflower crops). Winter wheat is generally more tolerant than spring wheat.
In field trials, sulfosulfuron gave equivalent or better control of weeds at less than 1% of the application rate of isoproturon. Monsanto says that the product fits well with its Ecotillage conservation farming system.
A metabolism study (Weed Science, 2000) using radiolabelled material showed that sulfosulfuron is rapidly metabolised in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum) whereas the weed species wild oat (Avena fatua), jointed goatgrass (Aegilops cylindrica) and downey brome (Bromus tectorum) metabolised the herbicide significantly slower with wild brome being the most susceptible and jointed goatgrass the least.
Sulfosulfuron (35 g/ha) was tested for efficacy on downy brome (Bromus tectorum) and cheat (Bromus secalinus) in winter wheat crops in Kansas and Wyoming,1998-2001 (Weed Technology, 2002). Control of both species from fall and early spring applications was excellent. Late spring application was sometimes less effective and ran a risk of slightly stunting the crop.
Concerns over the potential for crop injury from sulfosulfuron residues in soils were investigated in field trials in Western Canada (Weed Technology, 2001). Soil organic matter (OM) levels and pH would be expected to affect the availability of sulfosulfuron and potentially synergistic activity with soil residues of other herbicides was recognised. Results indicated little potential for damage to canola in soils with OM levels greater than 4.5%. Sulfosulfuron, furthermore, should carry less risk of damage to following crops than triasulfuron. Effects of residues of other herbicides (eg triasulfuron, imazethapyr, metasulfuron) should be only additive.
In the UK, minimal tillage techniques can greatly reduce the cost of crop establishment, but Bromus species can become a major problem. On-farm use has shown that sulfosulfuron (Monitor) may only stunt bromes and prevent seeding rather than completely kill in some situations. Nevertheless, it is a useful tool and has the advantage over other products such as propoxycarbazone-sodium of allowing the safe sowing of oilseed rape as a following crop in the same year. It also has a superior spectrum of broad-leaved weeds controlled.
Monsanto recommend the use of Monitor in an integrated approach to the control of Bromus species (Farmers Weekly, 2003). Best levels of control will be found on meadow, rye and soft brome (B. commutatus, B. secalinus, B. hordeaceus, respectively), with slightly less effect on barren and great bromes (Anisantha sterilis, A. diandra, respectively). Cultural approaches and application with adjuvants (eg Frigate) at the time crop competition is greatest will give best results. Improvements in couch control will be achieved by using in conjunction with pre-harvest glyphosate. Better control of broad-leaved weeds, over-wintered grasses, or cleavers will come from tank-mixes with bromoxynil products, Topik, or Starane, respectively. Applications to crops which are waterlogged, or drought stressed, or during frosty conditions should be avoided. Winter barley on sandy soils and sugar beet should not follow in the rotation for one or two years, respectively, when Monitor has been used. -
CropUseCropUses:
potatoes, soybeans, triticale, turf, wheat
Wheat
10-35 g ai/ha
-
PremixMetsulfuron-methyl+sulfosulfuron
Type
AI concn
Water-dispersible granule (WG)
75% (w/w) 80% (w/w)
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:470.48; Physical form:White, odourless solid. Density:1.5185 (20 °C); Melting point:201.1-201.7 °C; Vapour pressure:<1 × 10-3 mPa; Henry constant:8.15×10-7 ( pH 5), 8.83 ×10-9 ( pH 7), 2.97 × 10-8 ( pH 9) ( calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP <1 ( pH 5 to 9 buffer); pKa:3.51 (20 °C); Solubility:In water 18 ( pH 5), 1627 ( pH 7), 482 ( pH 9) (all in ppm).;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant; moderate eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation:Practically non-toxic. Phytotoxicity:Barley and oats are sensitive. Tolerance of durum wheat is variety-specific.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:?
Algae: EbC50 (3 d) for green algae (Selenastrum capricornutum) 0.221 mg/l, ErC50 (3 d) 0.669 mg/l; EC50 (5 d) for bBees: LD50 (oral) >30 μg/bee; (dermal) >25 μg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) >96 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >95, carp >91, bluegill sunfish >96, minnow >101 mg/l.Worms:LC50 >848 mg/kg.Other aquatic spp.:IC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba (G3) >1.0 μg/l.Other beneficial spp.:Classified as harmless to Bembidion tetracolum, Paradosa spp., Typhlodromus pyri, Apidus rhopalosiphi.?
Environmental fate:?
Cleavage of the sulfonylurea linkage in soil is a major pathway of metabolism, with oxidative demethylation playing a significant role in some matrices.Animals:Sulfosulfuron was eliminated rapidly from rats, with limited metabolism and negligible residues in tissues. O-Demethylation to yield desmethyl sulfosulfuron and ring-hydroxylation on the pyrimidine ring were the primary metabolic pathways. Rapid Soil:The primary degradation pathway in soil is the hydrolytic cleavage of the sulfonylurea linkage to yield the corresponding sulfonamide and dimethoxypyrimidinamine. DT50 (lab.) 32 d (silt loam, pH 7.6, 0.8% Plant:Residues in wheat grain were negligible. The major component in wheat forage and straw from the post-emergent treatment was unmetabolised sulfosulfuron. The major metabolite, a sulfonamide, resulted from cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge.?
Mallard duck
LD50 >2,250 mg/kg Quail LD50 >2,250 mg/kg
Rainbow trout [96 h]
LC50 >95 mg/L Carp [96 h] LC50 >91 mg/L
Bee [oral 48 h]
LD50 >30 μg/bee Daphnia [48 h] LC50 >96 mg/L
Fate in soil:
Sulfosulfuron is degraded by hydrolysis and by microbial action in the soil. Its half-life is between 13 and 75 days, depending on field conditions. Sulfosulfuron is only slightly mobile in soil.Fate in aquatic systems:
Sulfosulfuron is degraded by hydrolysis and by microbial action. The half-life varies between 16 and 32 days depending on the type of system. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide
Related CompaniesMore
Country: India
Cypermethrin Permethrin Alpha-cypermethrin Fenvalerate Lambda-cyhalothrin Chlorpyrifos-methyl Ethion Phenthoate Bifenthrin Thiamethoxam
Country: India
Alpha-cypermethrin Cypermethrin Deltamethrin Permethrin Chlorpyrifos Indoxacarb Fipronil Diflubenzuron Diuron Triclopyr
Country: India
Acetamiprid Acephate Lambda-cyhalothrin Atrazine Hexaconazole Metalaxyl Metalaxyl+mancozeb Kresoxim-methyl Metribuzin Pendimethalin
Country: India
Country: India

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe