-
Common NameTecnazene
-
中文通用名四氯硝基苯
-
IUPAC1,2,4,5-tetrachloro-3-nitrobenzene
-
CAS1,2,4,5-tetrachloro-3-nitrobenzene
-
CAS No.117-18-0
-
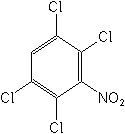
Molecular FormulaC6HCl4NO2
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityPlant Growth Regulator
Fungicide, plant growth regulator
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:260.9; Physical form:Colourless crystals. Density:1.744 (25 °C); Melting point:99 °C; Vapour pressure:240 mPa (15 °C); Solubility:In water 0.44 mg/l (20 °C). In ethanol c. 40 g/l (25 °C).; Stability:Very stable to acids and bases. Stable to heat up to almost 300 °C. In solution, decomposes slowly when exposed to u.v.irradiation.;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2047, female rats 1256 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant (rats). Slight/mild eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation:LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.74 mg/l. Phytotoxicity:Some varieties of rose are susceptible. ADI:(Japan) 0.058 mg/kg.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Bees:Non-toxic to bees.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) >0.58 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout (flow through) 0.37 mg/l.
Environmental fate:
Animals:In animals, following oral administration, tecnazene is rapidly absorbed and metabolised. High single oral doses are predominantly excreted unchanged in the faeces. Several metabolites are presumed in the urine, the most important being the mercapturic acSoil:In soil, tecnazene is rapidly lost, probably mainly through evaporation.Plant:In plants, substitution of the chlorine atoms by sulfhydryl groups has been observed. -
Transport InformationHazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe