-
Common NameTrifloxystrobin
-
中文通用名肟菌酯
-
IUPACmethyl (E)-methoxyimino-{(E)-α-[1-(α,α,α-trifluoro-m-tolyl)ethylideneaminooxy]-o-tolyl}acetate
-
CASmethyl (αE)-α-(methoxyimino)-2-[[[[(1E)-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylidene]amino]oxy]methyl]benzeneacetate
-
CAS No.141517-21-7
-
Molecular FormulaC20H19F3N2O4
-
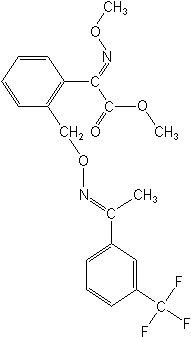
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityFungicide
Trifloxystrobin is active against ascomycetes, basidiomycetes, deuteromycetes and oomycetes, especially in the early stages in the infection cycle. Novartis coined the term ‘mesostemic’ to encapsulate all aspects of the product's activity on and in plants. Trifloxystrobin is applied to foliage and is strongly adsorbed to the waxy, cuticular layer of plants. Product that remains on the leaf surface acts as a protectant. Some product penetrates the cuticle and remains either just below the surface to provide curative activity or is distributed locally providing translaminar activity. However, it is not translocated in the vascular system.
It is safe to crops and shows no cross-resistance to fungicides from other chemical classes. The product has a greening effect on cereals that leads to increased yields.
Physiological studies into the effects of trifloxystrobin on the yield and protein content of wheat indicate that enhanced nitrogen metabolism may explain the maintenance of protein levels at higher yields, thus avoiding the dilution effect shown by other strobilurins (Pflanzenschutz-Nachrichten Bayer, 55). Trifloxystrobin, azoxystrobin and kresoxim-methyl increased flag leaf area, but levels of nitrate reductase were only increased by trifloxystrobin. In field trials, trifloxystrobin treatments extracted more soil nitrogen. No strobilurin affected photosynthesis, but only trifloxystrobin decreased transpiration, which suggests more efficient use of water.
It is recommended that trifloxystrobin is used primarily in a preventative spray schedule.
Trifloxystrobin also has activity via movement in the vapour phase, which contributes to disease control within the crop canopy.
In field trials, trifloxystrobin often gave better disease control than standard fungicide treatments (including other strobilurins) at similar or lower application rates. Novartis UK trials showed that crops treated with Twist out-yielded those treated with azoxystrobin in 67% of trials and those treated with kresoxim-methyl in 94% of trials. It is also stated that trifloxystrobin offers superior control of Septoria tritici and S nodorum on wheat, and Rhynchosporium secalis on barley compared to other strobilurins although the control of yellow and brown rust on wheat and brown rust and net blotch on barley is inferior to that given by azoxystrobin. In field trials carried out on cotton in the period 1997-2001, trifloxystrobin tank mixed with mefenoxam (D0082) was found to increase stand counts compared to other standard fungicides. Although there was no significant increase in yield, trifloxystrobin was found to control significantly more seedling disease.
Trifloxystrobin (code number USF 2004) has been tested in the US at 105 ml/ha plus 122 ml/ha of tebuconazole on cantaloupe and although it provided ‘fair’ control of powdery mildew, it was not as effective as triflumizole (D0001L). It has also been tested in combination with Induce (2.5 oz/a USF 2004 + 0.25% Induce) on powdery mildew in Kentucky bluegrass (NuGlade) with good results. USF 2004 (at 2 and 2.5 oz/ac) has been found to reduce the incidence of choke on Tiffany Chewings Fescue when used in combination with Folicur (2.31 and 2.88 oz/ac) and Induce (0.25%). It is also moderately effective for control of greasy spot (the efficiency is increased by the addition of petroleum oil) and melanose (in combination with copper products) on grapefruit.
In cereals, trifloxystrobin should be used in mixtures with triazoles; the company recommends mixtures with cyprodinil (D0037), cyproconazole or epoxiconazole (D0019). In fruit and vegetable crops, the product should be used as part of a spray programme alternating with fungicides with a different mode of action. The company states that trifloxystrobin is suitable for use in IPM programmes.
In vines, trifloxystrobin is active against black rot (Guignardia bidwelii), powdery mildew (Oidium spp), excoriose (Phomopsis viticola) and rotbrenner (Pseudopeziza tracheiphila), and demonstrates secondary effects against Botrytis. Residual activity is maintained for around 14 days.
Field trials conducted in turf (APS, 2002) showed that Compass or applications of trifloxystrobin plus fosetyl-Al or triadimefon provided good control of rapid blight. This disease has recently been identified as a potential major problem in turf where it can kill large areas of perennial ryegrass and rough bluegrass that are overseeded onto bermudagrass golf courses.
USF 2007 and USF 2010 are combinations of trifloxystrobin + tebuconazole. In 2001 and 2002, USF 2007 was tested on sugar beet for the control of cercospora leaf spot (cercospora beticola) and in 2002 on potato for the control of early blight (Alternaria solani). The results were comparable with those of other fungicides under evaluation. In 2003, USF 2010 was tested on almonds, peaches, peanuts, and sour cherries for the control of a variety of diseases, including brown rot, early and late leaf spot, leaf curl, powdery mildew, rhizopus rot, rust, rusty spot, scab, southern stem rot, web blotch. In most tests, the product compared well with other commercially available fungicides. -
CropUseCropUses:
almonds, apples, bananas, barley, calamint, citrus, cucurbits, grapefruits, hops, mangos, melons, nectarines, nuts, oats, ornamentals, peaches, peanuts, pears, pecans, pistachios, potatoes, rice, rye sugar beet, tea, turf, vines, wheat
Cereals
125-187.5 g ai/ha
Apples
3.75-7.5 g ai/hl
Peanuts
70-105 g ai/ha
Potatoes, sugar beet
104-140 g ai/ha
Vines
6.25-7.5 g ai/hl
Cucurbits
6.25-12.5 g ai/hl
Bananas
70-90 g ai/h
-
Disease SpectrumBroad spectrum fungicide against Alternaria spp., Cercospora spp., Colletotrichum spp., Mycosphaerella spp., powdery mildews, Pyricularia spp., Rhizoctonia solani, Rhynchosporium secalis, rusts, Septoria spp., Venturia spp. and various other leaf and fruit diseases.
-
FormulationDP = Dustable powder
SC = Suspension concentrate (=flowable concentrate)
WG = Water dispersible granules -
PremixTrifloxystrobin+triadimefon
Trifloxystrobin+tebuconazole
Trifloxystrobin+prothioconazole
trifloxystrobin+propiconazole+prothioconazole
Trifloxystrobin+propiconazole
Trifloxystrobin+Prochloraz
Trifloxystrobin+Oxine-copper
Trifloxystrobin+Metiram
Trifloxystrobin+metalaxyl+triadimenol
Trifloxystrobin+Isotianil
Trifloxystrobin+Hexaconazole
Trifloxystrobin+fluopyram
Trifloxystrobin+Ethirimol
Trifloxystrobin+cyproconazole
Trifloxystrobin+Cymoxanil
Thifluzamide+Trifloxystrobin
Tetraconazole+Trifloxystrobin
Oligosaccharins+Trifloxystrobin
Iprodione+Trifloxystrobin
Fluoxastrobin+prothioconazole+trifloxystrobin
Epoxiconazole+Trifloxystrobin
Dithianon+Trifloxystrobin
Difenoconazole+Trifloxystrobin
Clothianidin+carboxin+metalaxyl+trifloxystrobin
Captan+Trifloxystrobin
Boscalid+Trifloxystrobin
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:408.4; Physical form:Odourless, white solid. Melting point:72.9 °C; Vapour pressure:3.4 × 10-3 mPa (25 °C); Henry constant:2.3 × 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 4.5 (25 °C); Solubility:In water 610 µg/l (25 °C).; Stability:Hydrolysis DT50 11.4 w (pH 7); stable at pH 5. Aqueous photolysis DT50 31.5 h ( pH 7, 25 °C).; Grey to beige granules. Weak odor. Melting point 70.9°C.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits); may cause sensitisation by skin contact. Inhalation: LC50 for rats >4646 mg/m3.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Bees: LD50 (oral) >200 µg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg.Daphnia:LC50 (48 h) 0.016 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.015 mg/l.Worms: LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg soil.Other aquatic spp.:Toxic to aquatic organisms in laboratory tests. Considered low risk to aquatic ecosystems when used as recommended, due to low use rates and rapid dissipation in biotic environments.Other beneficial spp.:Harmless in normal use to a wide range of beneficial arthropods, including predatory mites, ground- and foliage- dwelling predators and parasitic wasps.
Environmental fate:
Animals:In rats, absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, rapidly metabolised and quickly and completely eliminated from the body.Soil:Dissipates rapidly from soil and surface water. Soil DT50 4.2-9.5 d. Koc 1642-3745. No leaching potential. In water, DT50 0.3-1 d, DT90 4-8 d.Plant:Rapidly degraded; metabolic profile is similar for a range of crops, with the parent and the acid metabolite being the relevant compounds for residues determination.
Mallard duck
LD50 >2,250 mg/kg
Bobwhite quail
LD50 >2,000 mg/kg
Rainbow trout [96 h]
LC50 0.014 mg/L
Daphnia
LC50 0.025 mg/L
Bluegill sunfish [96 h]
LC50 0.054 mg/L
Green algae
EC50 37 ppb
Earthworms
LD50 >1,000 mg/kg
Bees [oral]
LD50 >200 μg/bee
Fate in aquatic systems:
Hydrolysis occurs at pH >5. In surface water, trifloxystrobin is rapidly degraded within a few hours by microbial processes.Fate in soil:
Trifloxystrobin is degraded by microbial and photolytic processes in soil. It has a soil half-life under field conditions of 2-16 days. The product adsorbs strongly to soil particles (Koc = 1642-3745 ml/g) indicating limited potential for mobility in soil. The acid metabolite, CGA-321113, appears to be a mobile and persistent metabolite which is degraded at a slower rate than the parent compound. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Trifloxystrobin Prothioconazole Bixafen
Bayer released fungicide Cripton Xpro in Chile
Bixafen Prothioconazole Trifloxystrobin
Bayer launches fungicide to control major cotton disease in Brazil
Prothioconazole Bixafen Trifloxystrobin
EU renews approval for three pesticide active ingredients
Carfentrazone-ethyl Trifloxystrobin
Bayer launched new fungicide Exteris Stressgard via Rigby Taylor in UK
U.S. EPA OKs Bayer's new Exteris Stressgard fungicide
Australia approved 13 ais registrations (Special gazette, 9 December 2014)
Quinoxyfen Dimethomorph Trifloxystrobin Isoxaflutole Glufosinate-ammonium Hexazinone Fipronil Clothianidin Thiram Prothioconazole Thiacloprid Chlormequat chloride
Bayer introduces Delaro™ fungicide for 2015 growing season
Prothioconazole Trifloxystrobin
Related CompaniesMore
Jiangsu Sword Agrochemicals Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Triadimefon Triadimenol Tebuconazole Diniconazole Bitertanol Cyproconazole Propineb Paclobutrazol Metribuzin Bentazone
Shanghai Heben-Eastsun Medicaments Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Thiamethoxam Azoxystrobin Boscalid Chlorfenapyr Difenoconazole Fludioxonil Indoxacarb Picoxystrobin Pyraclostrobin Tebuconazole
Shandong Jingbo Agrochemicals Technology Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Pyrimethanil Pyraclostrobin Fomesafen Tebufenozide Fenoxanil Azoxystrobin Kresoxim-methyl Boscalid Nicosulfuron Emamectin benzoate Indoxacarb Quizalofop-P-ethyl
Rudong Zhongyi Chemical Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Pyraclostrobin Trifloxystrobin Prothioconazole tebuconazole pyriproxyfen cyproconazole cyazofamid famoxadone
Shenzhen Baocheng Chemical Industry CO.,LTD.
Country: China
Glyphosate Emamectin benzoate Lambda-cyhalothrin Pyraclostrobin Bromacil Glufosinate-ammonium Tembotrione Prothioconazole Topramezone Chlorantraniliprole

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe