-
Common NameZoxamide
-
中文通用名苯酰菌胺
-
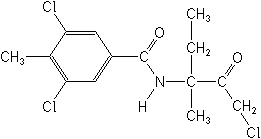
IUPAC(RS)-3,5-dichloro-N-(3-chloro-1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-oxopropyl)-p-toluamide
-
CAS3,5-dichloro-N-(3-chloro-1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-oxopropyl)-4-methylbenzamide
-
CAS No.156052-68-5
-
Molecular FormulaC14H16Cl3NO2
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
Activity
Fungicide
Zoxamide is primarily an oomycete fungicide although it has some activity against ascomycetes and basidiomycetes such as Venturia spp, Sclerotinia spp, Cercosporabeticola and Botrytis cinerea. The product has protectant and curative activity but higher application rates may be required when the product is applied curatively.
Zoxamide acts by disruption of the microtubule structure and inhibition of cell division. The mechanism for this activity is through the covalent binding of the active ingredient to β-tubulin in the cytoskeleton. There is no effect on encystment, germination or zoospore motility; however, it is proposed that zoxamide can cause a reduction in the production of viable motile zoospores. Scanning microscopy studies showed zoxamide action against blight on potato crops begins after germination, achieving inhibition of hyphal development and sporangia production. This novel mode of action makes zoxamide an important new tool in anti-resistance strategies. It is the first anti-tubulin fungicide to be used commercially against oomycetes.
Zoxamide has a strong affinity for the waxy cuticle of leaves leading to "exceptional" rainfastness. It has residual activity lasting for up to 15 days after treatment. In field trials, zoxamide controlled foliar, stem and tuber blight in potatoes. The product generally gave control equal or superior to that of established products, usually at lower application rates. A maximum of 6 applications can be made on potatoes, and 8 on grapes.
No cross resistance has been observed with other chemical types controlling Oomycete fungicides. A study of the product's effectiveness against potato blight (Phytophtora infestans) carried out on European crop isolates showed no development of resistance or decreased sensitivity to the product in crops previously exposed to zoxamide. Hence zoxamide is recommended for use in resistance and integrated crop management systems. -
CropUseCROP USES:
broccoli, cucurbits, lettuces, melons, onion, peas, potatoes, spinach, squash, tomatoes, vegetables, vines
Grapes140-224 g ai/haPotatoes146-190 g ai/ha
-
PremixZoxamide+mancozeb
zoxamide+chlorothalonilTypeAI concnSuspension concentrate (SC)24% (w/v)Wettable powder (WP)80% (w/w)
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:336.7g/mol;Melting point:159.5-160.5℃;V.p. <1×10-2 mPa (up to 45 ℃) KOW logP = 3.76 (20℃) Solubility In water 0.681 mg/l (20 ℃). Stability Aqueous hydrolysis DT50 c. 15 d (pH 4 and 7), c. 8 d (pH 9). Aqueous photolysis DT50 7.8 d.
-
ToxicologyOral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg.Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits); is a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).Inhalation LC50 >5.3 mg/l.
-
Environmental ProfileRainbow trout [96 h]LC50 160 μg/LBluegill sunfishLC50 >790 ppbDaphnia magnaEC50 >780 ppbBee [contact]LD50 >100 μg/beeSheepshead minnowLC50 >860 ppbEastern oysterLC50 >715 ppbMysid shrimpLC50 >75 ppbEarthwormLC50 >1,070 mg/kg soilBobwhite quailLD50 >2,000 mg/kgFate in :
On the basis of the acute results summarised above, the US EPA classified zoxamide as very highly toxic to saltwater invertebrates, highly toxic to freshwater fishes and freshwater / marine / estuarine invertebrates, practically non-toxic to estuarine / marine fishes.Fate in soil:
Zoxamide has a soil half-life of 2-10 days. It has low mobility in soil and is not expected to leach to groundwater (Koc = 1166-1224). Photodegradation on soil is not a significant factor in the dissipation of zoxamide (half lives in irradiated and dark control samples were similar, i.e. 10.2 days 11.7 days, respectively). During rainfall or irrigation, zoxamide may move away from the site of application by erosion or runoff on soil particles and by drift due to its high affinity for soil and sediment. Zoxamide is likely to be adsorbed to sediments and organic material if carried to surface waters.Fate in aquatic systems:
Zoxamide is rapidly degraded by both photolysis (half-life of 7.8 days) and hydrolysis. It has a half-life of 14 days in pH 4 buffer solution.
Hydrolysis (especially at pH 9), photodegradation in water, and degradation by microbes are the major routes of dissipation.
In the environmental risk assessment conducted by the US EPA, concerns over the toxicity of zoxamide to aquatic organisms and its persistence in the field were mitigated by modelling studies, which showed that the combination of low dose rates and low parent compound mobility would prevent surface water concentrations reaching the levels of concern. -
Transport InformationHazard Class:O (Obsolete as pesticide, not classified)
Porduct NewsMore
EU renews approval for four pesticide active ingredients
Bentazone Silthiofam Forchlorfenuron Zoxamide
Gowan USA Announces the Federal Registration for Zing!® Fungicide
Related CompaniesMore
Yingde Greatchem Chemicals Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Folpet Desmedipham Dazomet Captan Triticonazole Ipconazole Metconazole Boscalid Thifluzamide Ethofumesate

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe