-
Common NameCloransulam-methyl
-
中文通用名氯酯磺草胺
-
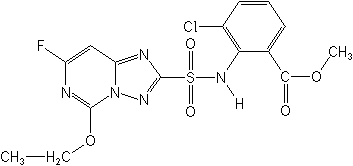
IUPACmethyl 3-chloro-2-(5-ethoxy-7-fluoro[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-ylsulfonamido)benzoate
or
methyl 3-chloro-N-(5-ethoxy-7-fluoro[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-ylsulfonyl)anthranilate -
CASmethyl 3-chloro-2-[[(5-ethoxy-7-fluoro[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-yl)sulfonyl]amino]benzoate
-
CAS No.147150-35-4
-
Molecular FormulaC15H13ClFN5O5S
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide.
Cloransulam-methyl is a systemic herbicide that is absorbed by roots and foliage before being translocated to the growing points; the meristem is the primary site of activity. The herbicide acts on the acetolactate synthase enzyme which plays a central role in the production of three amino acids which are required for cell division and growth. Cell division in roots and shoots slows or stops once the level of cloransulam-methyl becomes toxic.
Recommended treatments include pre-plant incorporated (PPI), pre-emergence or post-emergence up to the 50% flowering stage. When the herbicide is used pre-emergence, the roots and shoots come into contact with it as they grow - germinating seedlings may not emerge if they are in direct contact. In this instance, the availability and uptake of cloransulam-methyl are affected by soil moisture, texture, organic matter, pH, herbicide dissipation and plant growth rate. For post-emergent applications, the herbicide is quickly absorbed by the foliage and translocated to the shoot meristem. This causes sensitive seedlings to cease growing and slowly die.
FirstRate must be applied with a non-ionic surfactant at 0.25% v/v and liquid fertiliser at 2.5% v/v when applied as a post-emergent treatment.
Cloransulam-methyl can be tank-mixed with other herbicides for additional post-emergence broadleaf weed control. Monsanto recommends the use of Amplify in a tank mix with Roundup WeatherMax (a new product that will replace RoundUp UltraMax) for post-emergence applications on Roundup Ready soybeans. Dow recommends a tank mix of FirstRate with Glyphomax and Glyphomax Plus, its own brand glyphosate products, for use on Roundup Ready soybeans. FirstRate can be used alone or tank-mixed with Pursuit (with non-ionic surfactant and liquid fertiliser) for post-emergence applications to control Ambrosia trifida,Abutilon theophrasti,Datura stramonium and Xanthium strumarium; good residual control of broadleaf weeds is provided by such applications.
FirstRate has been approved for pre-emergence use with BroadStrike Dual (W0009.1), Dual 960 (W0123) and Pursuit for the control of Ambrosia artemisiifolia,Chenopodium album,Abutilon theophrasti and Xanthium strumarium. It can be used in conventional, reduced-tillage or no-tillage systems on most soil types.
Maize can be planted nine months and winter wheat four months after application of FirstRate. -
CropUseCrop uses:
Soybeans
Pre-emergence
35-44 g ai/ha
Post-emergence
17.5 g ai/ha
-
Premixflumioxazin+cloransulam-methyl
Water dispersible granules. Premix Parters: carboxin metalaxyl thiram.Type
AI concn
Water-dispersible granule (WG)
84% (w/w)
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:429.8; (acid 415.8); Physical form:Off-white powder. Density:1.538 (20 °C); Melting point:216-218 °C; Vapour pressure:4.0×10-11 mPa (25 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 1.12 (pH 5), -0.365 (pH 7), -1.24 (pH 8.5), 0.268 (distilled water); pKa:4.81 (20 °C); Solubility:In water 3 ppm (pH 5), 184 ppm (pH 7) (both 25 °C).; Stability:Stable to aqueous hydrolysis (pH 5), slowly degraded (pH 7), rapidly hydrolysed (pH 9). DT50for aqueous photolysis 22 min.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >3.77 mg/l.?
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:?
Algae:EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.00346 ppm.Bees: LD50 (contact) for honeybees >25 μg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg b.w. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm.Daphnia:LC50 (48 h) >163 mg/l.Fish:LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish >295, rainbow trout >86 ppm.Worms: NOEC (14 d) for earthworms 859 mg/kg soil.Other aquatic spp.:LC50 (96 h) for grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio) >121 mg/l; LC50 (48 h) for Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) >111 mg/l.Other beneficial spp.:Practically non-toxic. Environmental fate:?
Animals:In female rats, administered cloransulam-methyl is excreted mainly via the urine; in male rats, it is excreted in both urine and faeces. After 72 h, <0.1% of the dose was found in any tissue.Soil:Rapidly photolysed in water, DT50 22 min (pH 7). Photolysis on soil surface, DT50 30-70 d (corrected for metabolism). WATER SOLUBILITY: At 25°C: 3 ppm (pH5), 184 ppm (pH7).
Bobwhite quail
LD50 >2,250 mg/kg, practically non-toxic
Mallard duck
LD50 >2,000 mg/kg
Rainbow trout [96 h]
LC50 >86 mg/L slightly toxic
Bluegill sunfish [96 h]
LC50 >154 mg/L practically non-toxic
Daphnia magna[48 h]
LC50 98 mg/L slightly toxic
Bee [contact, 48 h]
LD50 >25 μg/bee relatively non-toxic
Green algae[5 d]
EC50 = 2.7 g/L
Earthworm [14 d]
LC50 >859 mg/kg soil no risk NOEC =116 mg/kg soil
Fate in soil:
Cloransulam-methyl is degraded by soil microorganisms. It has a laboratory soil half-life of 14-22 days under aerobic conditions. The parent compound is degraded by photolysis on soil with a half-life of 30-70 days. The observed metabolites suggest that microbial degradation and photolysis are the major routes of decomposition in the field. In the PMRA regulatory note (2001), the DT50 of cloransulam-methyl was found to be 6.6 days and the DT90 was 59.1 days in sandy loam soil under field conditions in Wisconsin. The maximum concentration of the acid metabolite was 25% of applied parent compound and was <10% at 100 days after application. The residues of cloransulam-methyl and the acid were detected primarily in the 0-30 cm soil layer. The lack of persistence of the parent compound may diminish the potential for cloransulam-methyl to contaminate groundwater.
The Koc of cloransulam in various soils is 15.8 - 87.1. The Koc for the acid metabolite is 57-135.3. Both compounds are classified as highly mobile in soil.Fate in aquatic systems:
Hydrolysis is pH dependent; parent cloransulam-methyl is stable at pH 5 (DT50 = >365 days) but is hydrolysed more rapidly at pH 7 (DT50 = 231 days) and pH 9 (DT50 = 3 days).
Aqueous photolysis is rapid with a half-life of 22 minutes at pH 7. In biotransformation studies, cloransulam-methyl has a half-life of 25.6 days in aerobic aquatic systems and 16 days in anaerobic aquatic conditions.
Due to the low octanol/water coefficient, cloransulam-methyl is not expected to bioaccumulate in fish.
Cloransulam-methyl and its major metabolite are considered mobile to highly mobile under field and laboratory conditions. In addition, the persistence of the parent and metabolites is likely to be longer as movement into the subsurface zones occurs. As a consequence of these regulatory concerns for parent and the biologically-active degradation products, the US EPA requested prospective groundwater monitoring and Tier II phytotoxicity studies as a condition of the registration of cloransulam-methyl. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III (Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
First Chinese company approved for cloransulam-methyl technical
US approved Dow’s new soybean herbicide Surveil®
Flumioxazin Cloransulam-methyl
Dow got ICAMA registration of cloransulam-methyl herbicide
Related CompaniesMore
Country: China
Glufosinate-ammonium 2,4-D MCPA Dicamba Propanil Clethodim Glyphosate Captan Flumioxazin Sulfentrazone
Jiangsu Agrochem Laboratory Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Florasulam Cloransulam-methyl Mesosulfuron-methyl Triflusulfuron-methyl Iodosulfuron-methyl Imazamox Halosulfuron Thidiazuron Flucarbazone-sodium Diclosulam
Beijing Bioseen Crop Sciences Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Diclosulam Cloransulam-methyl Florasulam Glufosinate-ammonium Pymetrozine+Dinotefuran Pyraclostrobin+thiophanate-methyl Pyraclostrobin+Thifluzamide Nitenpyram+Pymetrozine
SHANGHAI E-TONG CHEMICAL CO., LTD.
Country: China
Azoxystrobin Abamectin Cyproconazole Clothianidin Thiamethoxam Prothioconazole Emamectin benzoate Lufenuron Teflubenzuron

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe