-
Common NameCyhalofop-butyl
-
中文通用名氰氟草酯
-
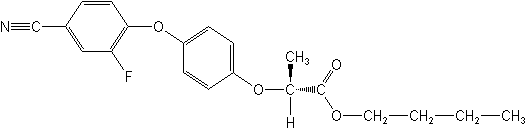
IUPACbutyl (R)-2-[4-(4-cyano-2-fluorophenoxy)phenoxy]propionate
-
CASbutyl (2R)-2-[4-(4-cyano-2-fluorophenoxy)phenoxy]propanoate
-
CAS No.122008-85-9
-
Molecular FormulaC20H20FNO4
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide.
Cyhalofop-butyl is active following absorption through the leaves. Weed growth stops immediately and the most recent leaves become necrotic within a week. Death occurs within 2-3 weeks depending on the weather and the size of the weeds. Cyhalofop-butyl will not control broadleaf weeds as the biochemical mode of action is specific to certain grasses.
Cyhalofop-butyl does not present any useful pre-emergence activity. It can be applied from germination to the four-leaf stage of barnyard grass with granular formulations, and from germination to the six-leaf stage with liquid formulations. It is rainfast within 2-3 hours and has no residual activity. The US product label states that 2.3 L/ha of crop oil concentrate should be added to the tank for all treatments. The product poses low risk to nearby crops such as cotton, soybeans and vegetables but Dow advises that drift to more sensitive crops such as maize, nectarines, peaches, sugar cane and sorghum should be avoided.
The selectivity of rice to cyhalofop-butyl is due to rapid metabolism (half-life less than 10 hours) in this crop to the inactive dicarboxylic acid resulting from hydrolysis of the ester and nitrile groups. By contrast, the major initial metabolic step in susceptible grasses is the rapid formation of the herbicidally active monocarboxylic acid (80% formed within 10 hours) by hydrolysis of the ester group.
Dow AgroSciences recommends that for dry-seeded rice, Clincher should be applied to 1-4 inch weeds pre-flood at a rate of 280 g/ha or post-flood at 280-312 g/ha for control of large grasses prior to heading. For water-seeded rice, the product should be applied when the weeds are at least 50% exposed, and the fields should be reflooded 24-48 hours after application if drained.
Research carried out at the California Rice Research Board found that cyhalofop-butyl has a better safety margin than Whip but may face use limitations in areas where Echinochloa is developing resistance to ‘fop’ herbicides such as Whip. However, it may be used in situations where propanil- or quinclorac-resistant Echinochloa is present. Application of Clincher at the three-leaf stage, followed by trichlopyr (Grandstand) at mid-tillering was found to provide broad spectrum control, whilst tank mixtures of cyhalofop and propanil were found to control Echinochloa spp, Cyperus compressus and Leptochloa chinensis.
Field studies carried out in Vietnam by the Cuulong Delta Rice Research Institute found that a tank mix of cyhalofop-butyl at 60-80 g ai/ha and ethoxysulfuron at 12 g ai/ha provided effective control against all common weeds present in rice fields such as Echinochloa crus-galli, E colona, Leptochloa chinensis, Cyperus difformis, Fimbristylis miliacea, Ludwigia octovalvis, L adscendens and Marsilea minutaI. A higher rate of cyhalofop-butyl, applied as a late post-emergence spot treatment at 160-200 g ai/ha, provided control of perennial weeds Paspalum distichum and Echinochloa stagmina while retaining good activity in the rice crop.
Tank mixes with pendimethalin (Pendimax), quinclorac (Facet) or clomazone (Command) provide additional weed control. In France, Dow recommends that Clincher can be tank mixed or used in sequence with other herbicides for broad spectrum weed control, but not propanil-based products or sulfonylureas.
In it's first season in US rice (2003), Clincher performed well under conditions of high grass pressure; applications made at 7-10 days post-flood provided more consistent weed control than treatments made on drier soils at pre-flood. Excellent selectivity was observed on the rice.
An evaluation of herbicides on rice conducted by University of Arkansas found that an application of cyhalofop-butyl should be made within 2 weeks following flood establishment in rice fields in order to maximise efficacy on grass weeds. -
CropUseCrop uses:
rice
Granular formulation: 280 - 310 g ai/ha
Liquid formulation: 1-1.1 L/ha
-
PremixQuinclorac+Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl+Cyhalofop-butyl
Pyribenzoxim+Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl+Cyhalofop-butyl
Pyribenzoxim+Pretilachlor+Cyhalofop-butyl
Pyribenzoxim+cyhalofop-butyl
Penoxsulam+Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl+Cyhalofop-butyl
Penoxsulam+Pretilachlor+Cyhalofop-butyl
Penoxsulam+Cyhalofop-butyl+Pyribenzoxim
Penoxsulam+Cyhalofop-butyl+Fluroxypyr-meptyl
Penoxsulam+cyhalofop-butyl
Penoxsulam+Carfentrazone-ethyl+Cyhalofop-butyl
Penoxsulam+Bispyribac-sodium+Cyhalofop-butyl
Cyhalofop-butyl+Pyribenzoxim+Bentazone
Cyhalofop-butyl+Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl+Bispyribac-sodium
Cyhalofop-butyl+Metamifop
Cyhalofop-butyl+Fluroxypyr-meptyl
Cyhalofop-butyl+Florpyrauxifen
Cyhalofop-butyl+Clomazone+Fluroxypyr-meptyl
Cyhalofop-butyl+Bispyribac-sodium
Bensulfuron-methyl+Penoxsulam+Cyhalofop-butyl
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:357.4. Physical form:White crystalline solid. Density:1.172 (20 °C); Composition:Material is the resolved (R)- isomer. Melting point:50 °C; Vapour pressure:1.2×10-3 mPa (20 °C); Henry constant:9.51×10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.31 (25 °C); Solubility:In water 0.44 (unbuffered), 0.46 (pH 5), 0.44 (pH 7.0) (all mg/l, 20 °C). In acetonitrile >250, n-heptane 6.06, n-octanol 16.0, dichloroethane >250, methanol >250, acetone >250, ethyl ac; Stability:Stable at pH 4, hydrolysed slowly at pH 7. At pH 1.2 or pH 9, decomposition is rapid.? 20°C: in acetonitrile, acetone, dichloroethane, methanol all >250 g/l; n-heptane 6 g/l; n-octanol 16 g/l.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats, and for male and female mice >5000 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Inhalation: LC50 for rats >5.63 mg/l. ADI:0.02 mg/kg b.w.?
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:?
Algae:EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum >1, Navicula sp. 0.64-1.33 mg/l. Soil and plant transformation products are less toxic to Selenastrum capricornutum.Bees:NOEC for honeybees >100 μg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 ppm.Daphnia:LC50 >100 mg/l.Fish:LC50 for rainbow trout >0.49, bluegill sunfish 0.76 mg/l. These values are at or above the aqueous solubility of cyhalofop-butyl.Worms:LD50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg.Other aquatic spp.:EC50 for eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) 0.52, scud (Gammarus sp.) 0.81 mg/l. These values are at or above the aqueous solubility of cyhalofop-butyl. Environmental fate:?
Animals:Rats, dogs, ruminants and poultry readily metabolise cyhalofop-butyl by hydrolysis to the acid. Depending on the animal, the acid may also break down to other metabolites. The acid and any additional degradates are then rapidly excreted. Residue levels ofSoil:Laboratory metabolism and field dissipation studies show that cyhalofop-butyl is rapidly metabolised in soil and sediment/water systems to cyhalofop acid; in the field, cyhalofop-butyl DT50 2-10 h in soil, <2 h in sediment/water. WATER SOLUBILITY: 0.44 mg/l (unbuffered), 0.46 mg/l (pH 5), 0.44 mg/l (pH 7) (all at 20°C).
Bobwhite quail [8 d]
LC50 >5,620 ppm Relatively non-toxic
Rainbow trout [96 h]
LC50 0.49 ppm Highly toxic
Daphnia magna [48 h]
LC50 0.58 ppm Highly toxic
Bee [48 h, contact]
LD50 >100 μg/bee Relatively non-toxic
Mallard duck [8 d]
LC50 >5,620 ppm Relatively non-toxic
Oyster [96 h]
LC50 0.52 ppm Moderately toxic
Bluegill sunfish [96 h]
LC50 0.76 ppm Highly toxic
Earthworm
LD50 >1,000 mg/kg
Fate in :
The EU SCP found that ground applications of cyhalofop-butyl to flooded or drained paddy fields at a maximum rate of 300 g ai/ha are unlikely to pose an unacceptable risk to aquatic organisms in adjacent surface water. In field studies, cyhalofop-butyl residues were below detection limits within 10 hours after application. However, all aerial applications and applications to flooded fields may pose an unacceptable risk to aquatic organisms in the paddy field. Additionally, no unacceptable risk to bees was observed, although there remains some uncertainty with other non-target arthropods which has yet to be addressed.
The EPA Fact Sheet advises not to use cyhalofop-butyl in areas where soils are permeable or where the water table is shallow, as this can result in water contamination.Fate in soil:
It has a low mobility in soils (Koc 1581- 6170 ml/g) whilst cyhalofop acid, the major soil metabolite, is more mobile. Cyhalofop-butyl is rapidly degraded under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions to give several metabolites. Soil metabolism is a significant route of dissipation with cyhalofop-butyl having T < 4 h and the major soil metabolite (cyhalofop acid) having T < 1 day. The parent compound and its metabolites do not penetrate below 15 cm depth of soil.
Cyhalofop-butyl is not expected to accumulate or leach into ground water.
Fate in aqueous systems:
Cyhalofop-butyl is stable to hydrolysis at pH 5, has a half-life of 88 days at pH 7 but is rapidly hydrolysed at pH 9 (DT50 0.5 day).
The estimated environmental concentrations (EEC) of cyhalofop-butyl were determined using the SCI-GROW model and a model developed by the US EPA as the usual GENEEC model is not suitable for pesticide applications to rice. For the acute exposure scenario, the EEC is 36 ppb in a water-seeded paddy, and 25 ppb for surface water and 0.16 ppb for ground water in dry-seeded paddy. In calculation of the DWLOC (drinking water levels of comparison), an appropriate endpoint could not be identified and therefore cyhalofop-butyl is not expected to pose an acute risk. For chronic exposure, the EEC is 3.7 ppb for water-seeded rice and 2.6 ppb for dry-seeded rice. As the chronic DWLOC (350 ppb) is greater than the EEC, cyhalofop-butyl is not expected to pose a risk. -
Transport InformationHazard Class:O (Obsolete as pesticide, not classified)
Porduct NewsMore
Corteva Agriscience launches two products for rice sector in Brazil
Tricyclazole Tebuconazole Cyhalofop-butyl Penoxsulam
More US registration reviews planned
Cyhalofop-butyl Diclofop-methyl Fluroxypyr Imazapic Noviflumuron Tebufenpyrad Etoxazole Polyoxin d zinc salt
Related CompaniesMore
Anhui Fengle Agrochemical Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Tribenuron-methyl Dimethomorph Bentazone Carboxin Quizalofop-P-ethyl Nicosulfuron Clomazone Propiconazole Chlorpyrifos Clopyralid Clodinafop-propargyl
Jiangsu Aolunda High-tech Industry Co.,Ltd
Country: China
Tri-allate EPTC Thiobencarb Molinate Prosulfocarb Dicamba Cyhalofop-butyl Diclosulam Spirodiclofen
Xuzhou Jinhe Chemical Co.,Ltd.
Country: China
Thiabendazole Metaldehyde Niclosamide Olamine Tricyclazole Brassinolide Chlorfenapyr Quizalofop-p-ethyl Cyhalofop-butyl LUFENURON Paraquat Dichloride
Shandong Kangqiao Bio-technology Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Pyraclostrobin+boscalid Pyraclostrobin+metiram Pyraclostrobin+epoxiconazole Thifluzamide Spiromesifen Spirodiclofen Pyraclostrobin
SINO AGRO-CHEMICAL INDUSTRY LTD.
Country: China
Prothioconazole Azoxystrobin Pyraclostrobin Methoxyfenozide Bifenazate Bispyribac-sodium Nicosulfuron Tebuconazole Pyribenzoxim Penoxsulam

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe