-
Common NameEthiprole
-
中文通用名乙虫腈
-
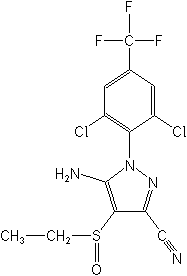
IUPAC5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-a,a,a-trifluoro-p-tolyl)-4-ethylsulfinylpyrazole-3-carbonitrile
-
CAS5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-ethylsulfinyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
-
Molecular FormulaC13H9Cl2F3N4OS
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityEthiprole is a broad-spectrum insecticide effective at low application rates against plant hoppers, thrips, aphids, weevils, flies and maggots, grasshoppers, psyllids, leaf miners and some species of whitefly. Good activity against stink bugs in rice has been reported.
The mode of action of ethiprole is different from many other insecticides including pyrethroids, organophosphates, chloronicotinyls and carbamates and there is little potential for cross-resistance with those classes. Consequently, ethiprole has good potential for use in insect-resistance management programmes where it can be used with other insecticide families in alternate spray programmes, tank-mix combinations or premixes.
A repellent effect against certain insects has been noted for ethiprole. The effect has been observed with termites, cockroaches, rice bugs and wireworms. Selective toxicity is due to the higher potency of ethiprole in the insect than in vertebrates.
Small-scale field trials of RPA 107382 applied as a water-based formulation to rangeland infestations of grasshoppers showed that a dose rate of 12 grams ai/acre (29.6 g ai/ha) resulted in 90% insect control with relatively little effect to beneficial species. The effects on the target species lasted for 21-28 days after treatment.
Small plot field trials in citrus in 1997 suggested that RPA 107382 could have potential for control of thrips.
Tests were conducted in the US with ethiprole as a potential organophosphate replacement for control of pests in stored wheat and corn (J Econ. Entomol., 2002). Ethiprole alone and in combination with other insecticides was shown to provide good pest control over the trial period of 6 months, regardless of the storage temperature.
A laboratory bioassay was conducted to evaluate the potential of ethiprole to control wireworms in germinating sugarcane. The results (J. Am. Soc. Sugarcane Tech., 2003) were not positive. -
CropUseCropUses:
alfalfa, citrus, cotton, ornamentals, peanuts, pome fruits, rice, soybeans, tea, vegetables
-
PremixEthiprole+Isoprocarb
-
Toxicology
Acute oral (rat) :LD50 >2,000 mg/kg
-
Environmental Profile
Fate in :
Ethiprole shows very low acute and subchronic toxicity to birds, low acute toxicity to fish, low acute and chronic toxicity to daphnia and high acute toxicity to mysid shrimp.
Ethiprole is relatively toxic to bees by ingestion or topical application and foliar applications are not recommended when bees are present.
Ethiprole is not toxic to earthworms.Fate in soil:
In preliminary studies ethiprole possesses a short half-life in soil. The parent ethiprole shows potential to leach whereas the metabolites possess moderate to low soil mobility. -
Transport InformationHazard Class:O (Obsolete as pesticide, not classified)
Porduct NewsMore
Bayer launches two rice seed treatment products in Japan
Related CompaniesMore
Yifan Biotechnology Group Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Fipronil Difenoconazole Metalaxyl Picoxystrobin Oxyfluorfen Clethodim Clodinafop-propargyl Metalaxyl-M Flumioxazin Prothioconazole
Country: China
Clethodim Hexazinone Mesotrione Abamectin Acetamiprid Dimethoate Fipronil Imidacloprid Fosetyl-aluminium 2,4-D

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe