-
Common NameCopper sulfate
-
中文通用名硫酸铜
-
IUPACcopper(II) tetraoxosulfate
or
copper(2+) tetraoxosulfate
or
cupric sulfate -
CASsulfuric acid copper(2+) salt (1:1)
-
CAS No.7758-98-7
-
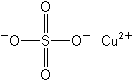
Molecular FormulaCuO4S
-
Molecular Structure
-
CategoryHerbicides > Inorganic herbicides
Fungicides > Copper fungicides
Algicides > Algicides
Molluscicides > Molluscicides -
ActivityHerbicides, algicide, fungicide
-
PremixValidamycin+Copper sulfate
Various crystal sizes: medium, large liquid, powder (snow) form, granular, water soluble. Premix Parters: copper oxychloride sulfur; cymoxanil; mancozeb.
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:249.7 (pentahydrate). Physical form: Blue crystals with no odor. Density:2.286 (15.6 °C); Melting point:147 °C (dehydrates); Vapour pressure: Non-volatile; Solubility:In water 148 (0 °C), 230.5 (25 °C), 335 (50 °C), 736 (100 °C) (all in g/kg). In methanol 156 g/l (18 °C). Practically insoluble in most other organic solvents. Soluble in glycerine to give an emerald green colour.; Stability:Slowly efflorescent in air. On heating, loses two molecules of water of crystallisation at 30 °C, two more molecules at 110 °C, and becomes anhydrous by 250 °C. By the reaction of alkalis on aqueous solutions, copper oxide is produced. Absorbs moisture readily when exposed to air. Phyton-27*: Thick greenish-brown liquid with pleasant odor.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 difficult to determine, since oral intake leads to nausea.(Rat): Oral LD50 472 mg/kg. Percutaneous: Causes severe skin irritation.Corrosive to eyes. Inhalation:LC50 for rats 1.48 mg/kg. Phytotoxicity: Phytotoxic to most plants when not mixed with lime to form Bordeaux mixture (q.v.).
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology: Bees:Toxic to bees.Birds:Less toxic to birds than to other animals. Lowest lethal dose for pigeons 1000 mg/kg, for ducks 600 mg/kg.Daphnia: EC50 (14 d) 2.3 mg/l; NOEC 0.10 mg/l.Fish:Very toxic to fish.LC50 31 mg/l (rainbow trout). Environmental fate: Animals:Copper is an essential element and is under homeostatic control in mammals.Soil:Copper is strongly adsorbed to surfaces of minerals and organic matter, hence soil mobility is very low. In water, copper ions have a strong tendency to form complexes or to be adsorbed, followed by sedimentation. In the sediment, copper reacts with organPlant:Plants resist copper accumulation and translocation to stems, leaves or seeds. Most plants growing on soils containing up to 1000 ppm copper showed only slight elevation in copper content compared to plants grown in normal soils. WATER SOLUBILITY: 230.5 g/kg at 25° C.
-
Transport InformationSignal Word:DANGER; Hazard Class:Ib (Highly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide
Related CompaniesMore
Country: India

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe