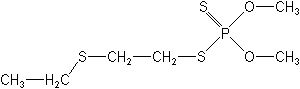-
Common NameThiometon
-
中文通用名甲基乙拌磷
-
IUPACS-2-ethylthioethyl O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
-
CASS-[2-(ethylthio)ethyl] O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
-
CAS No.640-15-3
-
Molecular FormulaC6H15O2PS3
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityInsecticide, acaricide
-
PremixEmulsifiable concentrate, ULV. Premix Parters: benomyl; carbendazim; carbendazim cymoxanil oxadixyl; carboxin; carboxin clothianidin metalaxyl; carboxin metalaxyl; imidacloprid; iprodione; isofenphos; metalaxyl thiabendazole; prochloraz; tebuconazole; thiophanate-methyl; tolclofos-methyl; triadimenol; vinclozolin;
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:246.3; Physical form:Colourless liquid, with characteristic odour of sulfur-containing organophosphate esters.Boiling point 110°C at 0.1 mm Hg. At 20°C: Vapor pressure 23 mPa, specific gravity 1.209. Density:1.209 (20 °C); Vapour pressure:39.9 mPa (20 °C); Henry constant:2.840 × 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 ( calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.15 (mean, 20 °C); Solubility:In water 200 mg/l (25 °C). Readily soluble in common organic solvents. Slightly soluble in petroleum ether and mineral oils.; Stability:Good stability when in non-polar solvents, more unstable in the pure state. Easily hydrolyzed in aqueous solution at 25°C, 50% loss in 25 days at pH 3, 27 days at pH 6, 17 days at pH 9.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male rats 73, female rats 136 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats 1429, female rats 1997 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant. Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) in rats 1.93 mg/l air (actual value for 'Ekatin 50ZP'). Phytotoxicity:Non-phytotoxic, except for some ornamentals.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae:EC50 (96 h) for green algae 12.8 mg/l.Bees:Toxic to bees; LD50 (oral) 0.56 µg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 (14 d) for male mallard ducks 95, female mallard ducks 53 mg/kg. Acute LD50 (14 d) for male Japanese quail 46, female Japanese quail 60 mg/Daphnia: LC50 (24 h) 8.2 mg/l.Fish:LC50 (96 h) for carp 13.2, rainbow trout 8.0 mg/l (both under static conditions).Worms: LC50 (7 d) 43.94 mg/kg soil; (14 d) 19.92 mg/kg soil.
Environmental fate:
Animals:Metabolism in animals is the same as in soil. Metabolism in rats showed that thiometon is rapidly and almost completely metabolised and excreted, mainly via urine. Metabolism proceeds via the conversion of P=S to P=O, oxidation of the sulfide to sulfoxideSoil:In soil, thiometon is metabolised to thiometon sulfoxide and thiometon sulfone. Thiometon: Koc 579 ml/g (low mobility), DT50 <1 d; thiometon sulfone: Koc 52 ml/g (highly moPlant:Oxidation and hydrolytic reactions are the most important factors in degradation. The main metabolites are thiometon sulfoxide and thiometon sulfone. The corresponding P=O analogues occur only in very small quantities. -
Transport InformationHazard Class:Ib(Highly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe