-
Common NameFenitrothion
-
中文通用名杀螟硫磷
-
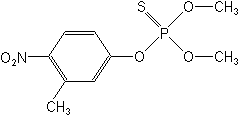
IUPACO,O-dimethyl O-4-nitro-m-tolyl phosphorothioate
-
CASO,O-dimethyl O-(3-methyl-4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate
-
CAS No.122-14-5
-
Molecular FormulaC9H12NO5PS
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityInsecticide/Acaricide/Miticide
-
PremixLambda-cyhalothrin+fenitrothion
Flucythrinate+fenitrothion
Fenvalerate+fenitrothion
Fenpropathrin+fenitrothion
Fenitrothion+deltamethrin
Fenitrothion+Acetamiprid
Esfenvalerate+fenitrothion
Cypermethrin+fenitrothion
Dust, emulsifiable concentrate, flowable, fogging concentrate, granules, oil-based liquid spray, ULV, wettable powder.
Premix Parters: fluazifop-P-butyl; iodosulfuron-methyl-sodium; isoproturon;
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:277.2; Physical form:Yellow-brown liquid, with a faint characteristic odour. Density:1.328 (25 °C); Melting point:0.3 °C; Flash point:157 °C; Vapour pressure:18 mPa (20 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.43 (20 °C); Solubility:In water 14 mg/l (30 °C). Readily soluble in alcohols, esters, ketones, aromatic hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons. In hexane 24, isopropanol 138 (both in g/l, 20 °C).; Stability:Relatively stable to hydrolysis under normal conditions: DT50 ( est.) 108.8 d ( pH 4), 84.3 d ( pH 7), 75 d ( pH 9) (22 °C).
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male rats c. 1700, female rats 1720 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats c. 810, female rats 840 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >2210 mg/m3 (aerosol). Phytotoxicity:Non-phytotoxic when used as recommended. Cotton, brassicas, and some fruits may be injured by high rates of application. Russetting is possible with some apple varieties. ADI:0.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae: EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 1.3 mg/l.Bees:Toxic to bees.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for quail 23.6, mallard ducks 1190 mg/ kg.Daphnia: EC50 (48 h) 0.0086 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (48 h) for carp 4.1 mg/l. LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 2.5, rainbow trout 1.3 mg/l.Other beneficial spp.:Highly toxic to non-target arthropods.
Environmental fate:
Animals:Fenitrothion is rapidly excreted in the urine and faeces. After 3 d, c. 90% has been excreted by rats, mice and rabbits. The most important metabolites are dimethylfenitrooxon and 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol.Soil: DT50 12-28 d under upland conditions, 4-20 d under submerged conditions. The major metabolites under upland conditions are 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol and CO2, whereas, under submerged conditions, the major decomposition pPlant:Fenitrothion applied in the forest (balsam fir and spruce foliage) degraded, with DT50 4 d; 70-85% is degraded within 2 weeks. Similar results are obtained in conifer foliage and cocoa trees. Major metabolites are 3-methyl-4-nit -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:II(Moderately hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe