-
Common NameFlazasulfuron
-
中文通用名啶嘧磺隆
-
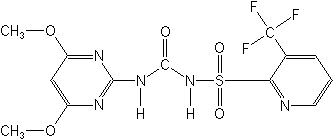
IUPAC1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-(3-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridylsulfonyl)urea
-
CASN-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinesulfonamide
-
CAS No.104040-78-0
-
Molecular FormulaC13H12F3N5O5S
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide
Flazasulfuron can be applied as a foliar spray or to the soil in warm-season turf. The optimum timing for applications is early post-emergence, but it also has some pre-emergence activity due to significant uptake by roots. Following applications to the soil, flazasulfuron provides residual control of annual weeds for between 30 and 90 days depending on the temperature. Following foliar applications, the product is absorbed by the leaves and translocated basipetally. Weed growth is immediately stunted, necrosis of the foliage is obvious within seven days and death occurs within 25 days. Rain and mowing just after application can reduce the efficacy of the product. The weed control spectrum is broad, including annual broadleaved and grass weeds and some biannual species. Efficacy in post-emergence applications can be extended by use of a partner such as sulfosate.
Cool-season turfs and some warm-season turfs are severely damaged by flazasulfuron. It is best tolerated by Cynodon spp and Zoysia spp.
Flazasulfuron is the first sulfonylurea registered for use in vines; this is attributable to rapid in-vivo metabolism which allows the vine to detoxify the herbicide. Extensive crop safety trials over a number of years have confirmed the selectivity at double the normal dose rate in various grape varieties, culture regimes and soil types. Studies have shown no detectable residues in grapes or vines. Applications should avoid contact with the leaves of the vine and should not be made to vines younger than 4 years.
In the French non-crop market, flazasulfuron has been shown to provide up to 6 months residual activity when applied at 50 g ai/ha in the parks, gardens, pavements and railway lines sectors, alone or in combination with a burndown partner such as sulfosate.
A study conducted in 2002-2003 showed that when a mixture of flazasulfuron and Induce, a non-ionic surfactant, was applied to annual bluegrass (Poa annua) in established turfgrass in December, it gave over 90% control. -
CropUseCropUses:
citrus, gardens, highways, olives, parks, sugar cane, tomatoes, turf, vines
Sugar cane: 25-100 g ai/ha
Turf: 25-100 g ai/ha
Vines: 50 g ai/ha
Non-crop: 50 g ai/ha
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:407.3; Physical form:Odourless, white crystalline powder. Density:1.6055 (20 °C); Composition:Tech. is ×92.0%. Melting point:166-170 °C; Flash point:Non-flammable; Vapour pressure:<0.013 mPa; Henry constant:<2.58 × 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1; Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = -0.06 (unstated pH); pKa:4.37 (20 °C); Solubility:In water 2.1 g/l ( pH 7, 25 °C). In octanol 0.2, methanol 4.2, acetone 22.7, toluene 0.56, acetonitrile 8.7 (all in g/l, 25 °C); in hexane 0.5 mg/l (25 °C).; Stability: DT50 in water 11 d (25 °C).;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Moderately irritating to eyes; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats 5.99 mg/l. Phytotoxicity:Transient discolouration of newly developing leaves and stunting may sometimes occur after treatment of turf, but recovery is rapid and complete.
-
Environmental Profile
Ecotoxicology:
Bees: LD50 >100 mg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >2000 mg/ kg.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) >20 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (48 h) for carp >20 mg/l.
Environmental fate:
Flazasulfuron does not present a risk of bioaccumulation in organisms. There is no negative effect towards soil microorganisms (respiration, nitrification).Fate in soil:
The half-life of flazasulfuron in soil is 13-16 days. The principal route of degradation in the soil is chemical hydrolysis though there is some contribution from microbial processes. Photolysis does not play a significant role in the decomposition of flazasulfuron.
Flazasulfuron is not strongly adsorbed to soils (the mean Koc in field soil studies is 46). However, the short soil persistence, coupled with the low application rate, acts to minimise the risk of groundwater and surface water contamination. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Canada proposes to approve herbicide flazasulfuron
Sapec Agro Portugal launches Zagaia herbicide
EU renews ISK Biosciences' herbicide flazasulfuron
Related CompaniesMore
Jiangsu Agrochem Laboratory Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Florasulam Cloransulam-methyl Mesosulfuron-methyl Triflusulfuron-methyl Iodosulfuron-methyl Imazamox Halosulfuron Thidiazuron Flucarbazone-sodium Diclosulam

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe