-
Common NameFlumioxazin
-
中文通用名丙炔氟草胺
-
IUPACN-(7-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-3-oxo-4-prop-2-ynyl-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-6-yl)cyclohex-1-ene-1,2-dicarboxamide
-
CAS2-[7-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-3-oxo-4-(2-propynyl)-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-6-yl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione
-
CAS No.103361-09-7
-
Molecular FormulaC19H15FN2O4
-
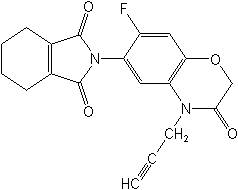
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide
Flumioxazin is a contact herbicide absorbed by foliage or germinating seedlings producing symptoms of wilting, necrosis and chlorosis within 24 hours of application. It controls annual and biennial broadleaf weeds and grasses; in regional studies in America, flumioxazin was found to control 40 broadleaf weed species either pre- or post-emergence. The product has residual activity lasting up to 100 days depending on conditions.
Flumioxazin acts by inhibition of protoporphyrinogen oxidase, an enzyme important in the synthesis of chlorophyll. It is suggested that porphyrins accumulate in susceptible plants, causing photosensitization that leads to membrane lipid peroxidation. The peroxidation of membrane lipids leads to irreversible damage of membrane function and structure in susceptible plants. The activity of flumioxazin is light and oxygen-dependent. Treatment of soil with flumioxazin will cause susceptible emerging plants to turn necrotic and die shortly after exposure to sunlight.
Flumioxazin can be used as a burndown treatment in reduced tillage cultivation systems in combination with glyphosate or other post-emergence products including Valent’s Select (clethodim). It can be applied prior to planting up to emergence of the crop but will cause severe damage to soybean if applied post-emergence of the crop. The product is highly selective to soybean and peanut when applied pre-emergence. In soybean field trials, flumioxazin gave equal or better control than metribuzin but at very much lower application rates.
In vineyards, flumioxazin is primarily for application pre-emergence of weeds. For post-emergence applications, mixtures with foliar herbicides are recommended. The product is only recommended for use on vines that are at least four years old.
Field trials were conducted in North Carolina to determine the effect of flumioxazin on weed control and cotton response. Post-emergence directed application of flumioxazin at 70 g ai/ha alone or mixed with glyphosate or MSMA provided complete control of common lambsquarters; common ragweed; entireleaf, ivyleaf, pitted and tall morningglory; Palmer amaranth; prickly sida; sicklepod; and smooth pigweed 4 weeks after treatment. Treatment with glyphosate at 1,120 g ai/ha was found to provide inferior control of sicklepod; entireleaf, ivyleaf, pitted and tall morningglory. Thus flumioxazin is effective against key weeds (including waterhemp (Amaranthus spp), velvetleaf (Abutilon threophrasti) and copperleaf (Acalypha ostryfolia) as well) that may escape treatments of glyphosate. Application of flumioxazin at 70 g ai/ha pre-plant between 0 and 10 weeks prior to planting was found to stunt cotton by 12% initially, and midseason cotton biomass was reduced on application at planting in 1 year. Post-emergence directed application at 36 or 70 g/ha did not injure 15 or 30 cm tall cotton.
Studies in cotton (Weed Science, 2003) following post-emergence applications of flumioxazin concluded that differential absorption, translocation and metabolism at various growth stages plus the development of a bark layer are the major reason for the tolerance of cotton to this herbicide.
Field and greenhouse trials have investigated the effectiveness of flumioxazin, both alone and in combination with S-metolachlor, as a pre-emergence herbicide for broadleaf weed control in potato. Over the range tested (0.035 to 0.07 kg/ha), flumioxazin was reported to have provided excellent control of broadleaf weeds, but for grasses the degree of control was rate dependent and improved by combination with S-metolachlor. Weed control and total yield was found to be comparable with sulfentrazone (W0035), metribuzin and rimsulfuron (W0011L). Flumioxazin is reported to be safe when applied to potato and to control several weed species common to potato production in the Western United States.
Studies carried out in Fort Collins, Torrington and Scottsbluff suggested that flumioxazin could be used to control broadleaf weeds in dry beans. Flumioxazin was applied at 0.034 to 0.135 kg ai/ha and whilst there was no significant crop damage at the Fort Collins and Torrington sites, that at Scottsbluff averaged 16% for rates above 0.068 kg ai/ha. Control of redwood was greater than 90% at all three locations and that of lambsquarter was ‘good to excellent’ at two sites. No significant difference in yield loss was reported.
The effectiveness of flumioxazin as a herbicide for strawberries has been tested in Oregon (USA). Application in May was found to provide excellent broadleaf control through early July and to August. Although red spots appeared on newly emerged leaves on plants treated with flumioxazin, subsequent growth was normal. Application in October provided excellent weed control through May. The timing of application did not affect yield and fruit size.
In 1996 and 1997, field studies were carried out to determine the effect of flumioxazin applied pre-emergence at 71 g ai/ha on seven Virginia-type peanut cultivars and an experimental breeding line. In 1996, visible injury 3 weeks after planting was 3% or less for all cultivars, whilst in 1997 it rose to 15 to 28% for all cultivars except one which exhibited 45% injury. However, no injury was visible at 5 and 9 weeks after planting.
The effect of flumioxazin on 15 soybean varieties in a greenhouse study and four varieties in the field was investigated over a 2 year period and the results compared to those of sulfentrazone (W0035). In the greenhouse study, there was 10% injury from sulfentrazone compared to 1% from flumioxazin. Application of sulfentrazone at the labelled rate reduced plant height 23 to 53% and caused 18 to 38% visible injury (stunting, crinkling of leaves, chlorotic spots) on the four sensitive varieties. In field experiments, the four varieties were treated with flumioxazin and sulfentrazone at 1, 2 and 4 X the labelled rates; injury was found to be similar for both herbicides. In 1998, emergence counts were reduced 27 to 73% with sulfentrazone and 19 to 52% with flumioxazin at the labelled rate. In 1999, emergence count reductions, stand count reductions and visible injury resulting from the herbicides were reduced compared to the previous year. Apart from one cultivar in 1999, the yields were not affected on using the labelled rate of herbicide. It is proposed that by not growing the sensitive varieties, the potential for injury and yield reduction on using these two herbicides will be reduced.
In field trials in Arizona (2000), flumioxazin gave good pre-em control of Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) in cantaloupe melons and Calsweet watermelons with good crop selectivity at the double rate. In further trials (2001), pre-em applications of flumioxazin caused significant injury to direct seeded dry bulb onions.
Flumioxazin can be tank mixed with clethodim, glyphosate, and paraquat for burndown application on peanuts, and can be tank mixed with dimethenamid, ethalfuralin, metolachlor, and pendimethalin for pre-emergence use on peanuts. For use on soybeans, flumioxazin can be tank mixed with clethodim, glyphosate, imazaquin, and paraquat for burndown applications, and with clomazone, cloransulam-methyl, imazaquin, imazethapyr, linuron, metribuzin, pendimethalin for pre-emergence applications.
Rotation to cotton, field corn, rice, sorghum, sunflower, tobacco or wheat is not advised for 30 days after application of 140 g/ha, or for 2 months after 210 g/ha. For both rates, rotation to barley, dry bean, rye or sweet corn is not advised for 4 months, or to alfalfa, canola, clover, oats, sugarbeet for 12 months after application. Use of flumioxazin on soybeans in the same field that flufenacet (W0077), alachlor, metolachlor (W0123) or dimethenamid (W0042L) will be used is not advised as soybean injury may occur.
Field trials in Hungary (2002) reported that pre-emergence applications of flumioxazin gave good control of Abutilon theophrasti and Datura stramonium with good selectivity in sunflower. The selectivity is partly positional; the herbicide forms a layer on the soil through which the vigorously germinating crop sprouts. The cotyledons are protected by the achenium while in contact with the soil.
BroadStar granules provide control of summer and winter annual grasses and broadleaved weeds in ornamentals. Over-the-top applications to container- or field-grown woody ornamental shrubs and trees provide residual control (8-12 weeks) of spurge, bittercress, oxalis, chickweed, groundsel, crabgrass, liverworts, eclipta, and phyllanthus. SureGuard is a sprayable formulation that can also be used on conifers, including Christmas trees. It is applied at any time up to weed emergence, or in post-emergence tank mixes with glyphosate. Residual control of 4-6 weeks is observed for control of chickweed, groundsel, dandelion, liverworts, lambsquarters, pigweed, allysum and ragweed. Valent reports that the dose rates applied in these products are 85% lower than other products used in the ornamentals sector.
Field trials on sugar cane in Louisiana in 2003 showed that flumioxazin gave superior control of morningglories to atrazine, and generally good levels of broadleaved weed control. However, although the crop recovered, levels of phytotoxicity were too high when applied post-emergence to the crop. Therefore, only applications to the soil at planting, or later directed applications were recommended. -
CropUseCropUses:
alfalfa, almonds, asparagus, barley, blueberries, celery, cotton, cucurbits, dry beans, maize, fruiting vegetables, garlic, grapevines, hop, mint, non-bearing fruits, nut trees, oats, ornamentals, peanuts, pecans, pistachios, pome fruit, potato, prickly pears, rice, shrubs, sorghum, soybeans, stone fruits, strawberries, sugarcane, sunflowers, sweet potatoes, tobacco, trees, vines, wheat
Peanuts
208 g ai/ha
Soybeans
138-208 g ai/ha
Ornamentals, trees, shrubs
167 kg/ha (BroadStar); 0.56-0.84 kg/ha (SureGuard)
Vines
600 g ai/ha
Sugar cane
210-280 g/ha (6-8oz/acre, max 12 oz/acre per season)
-
Premixthifensulfuron-methyl+flumioxazin+tribenuron-methyl
Flumioxazin+Pyroxasulfone+Chlorimuron
Flumioxazin+Pyroxasulfone
Flumioxazin+Pendimethalin
Flumioxazin+Glufosinate-ammonium
flumioxazin+cloransulam-methyl
Chlorimuron-ethyl+flumioxazin+thifensulfuron-methyl
Chlorimuron-ethyl+flumioxazin
chlorimuron+metribuzin+flumioxazin
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:354.3; Physical form:Yellow-brown powder. Density:1.5136 (20 °C); Melting point:201-204 °C; Vapour pressure:0.32 mPa (22 °C); Solubility:In water 1.79 g/l (25 °C). Soluble in common organic solvents.; Stability:Stable under normal storage conditions.;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; mild eye irritant (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >3930 mg/m3 air. Phytotoxicity:Soya beans and peanuts are tolerant. Maize, wheat, barley and rice are moderately tolerant.
-
Environmental Profile
Ecotoxicology:
Mallard duck: LD50 >2,250 mg/kg practically non-toxic;Rainbow trout [96 h]:LC50 = 2.3 mg/L moderately toxic;Bobwhite quail:LD50 >2,250 mg/kg practically non-toxic;Bluegill sunfish [96 h]:LC50 >21 mg/L slightly toxic;Honey bee: LC50 >105 μg/bee practically non-toxic;Daphnia pulex[96 h]: LC50 = 5.5 mg/L moderately toxic;Small mammals:LD50 >5000 mg/kg practically non-toxic;Sheepshead minnow [96 h]: LC50 >4.7 ppm moderately toxic;Eastern oyster [96 h]:LC50/EC50 =2.4 ppm moderately toxic;Mysid shrimp [96 h]:LC50/EC50 =0.23 ppm highly toxic
Environmental fate:
Fate in :
Flumioxazin is highly toxic to terrestrial plants; in seedling emergence studies lettuce is the most sensitive species (90 g ai/ha), with cucumber being the most sensitive in vegetative vigour studies (90 g ai/ha).Fate in soil:
Flumioxazin degrades rapidly in soils. Degradation is primarily due to microbial action (DT50 11.9 – 17.5 days (average 14.7 days) in aerobic soil) but hydrolysis and photolysis of the molecule also occurs; flumioxazin has a photolytic half-life of 3.2 to 8.4 days (average 5.8 days).
In unaged leaching studies, flumioxazin was found to be moderately mobile whilst in aged leaching studies it was generally not found at a depth greater than 3 inches.Fate in aquatic systems:
Flumioxazin is rapidly degraded in water by both photolysis (DT50 1 day at pH 5) and hydrolysis; it has a half-life of 4.2 days at pH 5, 1 day at pH 7 and 0.01 days at pH 9. Due to its instability, it is unlikely that flumioxazin will leach to groundwater. However, the potential for the degradation products APF and THPA to leach to groundwater is high. The mobility of the major degradation product, 482-HA, detected in the hydrolysis study and of the unidentified residues in the photolysis and anaerobic aquatic metabolism studies is unknown. The residues may persist in the environment and may leach to groundwater. It is possible that flumioxazin could reach surface water via spray drift or runoff under certain environmental conditions and so should not be applied where run-off is likely to occur.
Despite the potential for acute dietary exposure to flumioxazin in drinking water, the EPA does not expect flumioxazin to pose any significant health risks. The Estimated Environmental Concentrations (EECs) were 2.4 ppb for surface water and 6.3 ppb for ground water for the acute scenario. For the chronic scenario, the EEC was 0.67 ppb for surface water and 6.3 ppb for groundwater. These values were less than the lowest drinking water level of concern (DWLOC) values of 90 ppb for acute and 70 ppb for chronic exposure. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Corteva launches new soybean pre-emergent herbicide for 2021 season in US
Pyroxasulfone Metribuzin Flumioxazin
Flumioxazin – malignant weed destroyer with huge room for development
Nufarm launches Sumyzin 500 herbicide in liquid formulation in Brazil
Canada establishes MRL for flumioxazin in foods
Two new herbicides developed by Summit Agro now available in Argentina
Nufarm seeks to increase sales in Latin America next year
Yifan Biotechnology expands production capacity of herbicide Flumioxazin
Nufarm’s Clipper® Herbicide and 2,4-D registered in New Hampshire, US
US approved Dow’s new soybean herbicide Surveil®
Flumioxazin Cloransulam-methyl
Related CompaniesMore
Hangzhou Qingfeng Imp.& Exp. Co.,Ltd.
Country: China
S-metolachlor Fomesafen Flumioxazin Clethodim Imazapyr Tebuthiuron Azoxystrobin Tebuconazole Oxyfluorfen Metolachlor
Jiangyin Milagro Chemical Co.,Ltd
Country: China
Nuclear polyhedrosis virus Agriculural Organosilicone Adjuvant Amino acids seaweed formulation Ethephon Thiamethoxam+lambda-cyhalothrin Azoxystrobin + Difenoconazole Flumioxazin Indoxacarb Potassium Humate Enzymolysis Amino Acid Series
Shenzhen Baocheng Chemical Industry CO.,LTD.
Country: China
Glyphosate Emamectin benzoate Lambda-cyhalothrin Pyraclostrobin Bromacil Glufosinate-ammonium Tembotrione Prothioconazole Topramezone Chlorantraniliprole
Country: China
Glufosinate-ammonium 2,4-D MCPA Dicamba Propanil Clethodim Glyphosate Captan Flumioxazin Sulfentrazone
Country: China
Fluroxypyr-meptyl Clodinafop-propargyl Glufosinate-ammonium Picloram Clopyralid Triclopyr-butotyl Flumioxazin Triclopyr Diquat Epoxiconazole

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe