-
Common NameMethiocarb
-
中文通用名甲硫威
-
IUPAC4-methylthio-3,5-xylyl methylcarbamate
-
CAS3,5-dimethyl-4-(methylthio)phenyl methylcarbamate
-
CAS No.2032-65-7
-
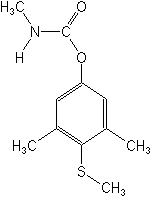
Molecular FormulaC11H15NO2S
-
Molecular Structure
-
CategoryInsecticides > Carbamate insecticides
Acaricides / Miticides > Carbamate acaricides
Repellents > Bird repellents
Molluscicides > Molluscicides -
ActivityMolluscicide, insecticide, acaricide, bird repellent
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:225.3; Physical form:Colourless crystals, with a phenol-like odour. Density:1.236 (20 °C); Melting point:119 °C; Vapour pressure:0.015 mPa (20 °C); 0.036 mPa (25 °C); Henry constant:1.2 × 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.08 (20 °C); Solubility:In water 27 mg/l (20 °C). In dichloromethane >200, isopropanol 53, toluene 33, hexane 1.3 (all in g/l, 20 °C).; Stability:Unstable in highly alkaline media. Hydrolysis DT50 (22 °C) >1 y ( pH 4), <35 d ( pH 7), 6 h ( pH 9). Soluble in 2-propanol, toluene. Hardly soluble in n-hexane.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats c. 20, mice 52-58, guinea pigs c. 40, dogs 25 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.3 mg/l air (aerosol); c. 0.5 mg/l (dust). Phytotoxicity:May lead to fruit thinning on apple trees, if applied earlier than four weeks after petal fall. ADI:0.001 mg/ kg b.w. [1997].
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae: ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 1.15 mg/l.Bees:Not toxic to bees (depending on mode of application).Birds:Acute oral LD50 for male mallard ducks 7.1-9.4, Japanese quail 5-10 mg/kg. LC50 (7 d) for bobwhite quail: no signs of toxicity as birds were repelled by 'Mesurol'.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 0.019 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.754, rainbow trout 0.436-4.7, golden orfe 3.8 mg/l.Worms: LC50 for Eisenia foetida >200 mg/ kg dry soil.
Environmental fate:
Animals:In dogs and mice, following oral administration, methiocarb is rapidly absorbed and excreted, principally in the urine, with only a small proportion in the faeces. Metabolism involves hydrolysis, oxidation, and hydroxylation, followed by excretion in freeSoil:Degradation in soil is rapid. The important metabolites are methylsulfinylphenol and methylsulfonylphenol.Plant:In plants, the methylthio group is oxidised to sulfoxide and sulfone, with hydrolysis to the corresponding thiophenol, methylsulfoxide-phenol, and methylsulfonyl-phenol (M. C. Bowman & M. Beroza, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1969, 52 -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
EU proposes not to renew approval of methiocarb
Test slug control options in spuds after methiocarb ban

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe