-
Common NameBiphenyl
-
中文通用名联苯
-
IUPACbiphenyl
-
CAS1,1′-biphenyl
-
CAS No.92-52-4
-
Molecular FormulaC12H10
-
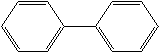
Molecular Structure
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:154.2; Physical form:Colourless crystals. Density:1.041; Melting point:69-71 °C; Flash point:106 °C; Solubility:Practically insoluble in water. Readily soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, and other organic solvents.; Stability:Very stable in acidic and alkaline media.;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats 3280, rabbits 2400, cats >2600 mg/kg. Depression of the central nervous system, paralysis, and convulsions have been observed in experimental animals. Inhalation:Prolonged exposure of humans to vapour concentrations >0.005 mg/l air is considered dangerous (J. Deichmann et al., J. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol., 1947, 29, 1). ADI:(JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg [1991].
-
Environmental ProfileEnvironmental fate:
Animals:In mammals, following oral administration, metabolites identified include 4-hydroxybiphenyl and other phenolic compounds (H. D. West et al., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1956, 60, 14-20).Plant:Residues in fruit have been reviewed (A. Rajzman, Residue Rev., 1964, 8, 1: S. W. Souci & G. Maier-Haarlder, ibid., 1966, 16, 103). -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION;
Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe