-
Common NameBitertanol
-
中文通用名联苯三唑醇
-
IUPAC(1RS,2RS;1RS,2SR)-1-(biphenyl-4-yloxy)-3,3-dimethyl-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol (20:80 ratio of (1RS,2RS)- and (1RS,2SR)-isomers)
-
CASβ-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yloxy)-α-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol
-
CAS No.55179-31-2
-
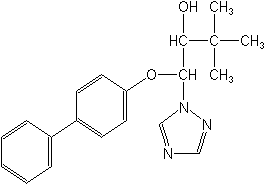
Molecular FormulaC20H23N3O2
-
Molecular Structure
-
Physical PropertiesColorless crystals; mixture of two diastereoisomeric enantiomer pairs (A.B). Vapor pressure A: 0.22 nPa, B: 2.5 nPa, at 20°C. Stable under normal storage conditions. Insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Very slightly soluble in isopropanol, toluene, methylene chloride, and cyclohexanone. Molecular weight:337.4; Physical form:White powder; (tech., white to tan crystals with a mild odour). Density:1.16 (20 °C); Composition:Bitertanol is a mixture of 2 diastereoisomers. Enantiomer A: (1R,2S) + (1S,2R); enantiomer B: (1R,2R) + (1S,2S) in the ratio A:B 8:2. Melting point:138.6 °C (A), 147.1 °C (B), 118 °C (eutectic of A and B); Vapour pressure:2.2 × 10-7 mPa (A); 2.5 × 10-6 mPa (B) (both 20 °C); Henry constant:2 × 10-8 Pa m3 mol-1 (A); 5 × 10-7 Pa m3 mol-1 (B) (both 20 °C, calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 4.1 (A), 4.15 (B) (both 20 °C); Solubility:In water 2.7 (A), 1.1 (B), 3.8 (eutectic) (all in mg/l, 20 °C, not affected by pH). In dichloromethane >250, isopropanol 67, xylene 18, n-octanol 53 (all for sum of A and B, in g/l, 20 °C).; Stability:Stable in neutral, acidic, and alkaline media; DT50 at 25 °C >1 y ( 4, 7 and 9).;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000, mice c. 4300, dogs >5000 mg/kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.55 mg/l air (aerosol), >1.2 mg/l air (dust). Phytotoxicity:Fruit crops are more tolerant to the wettable powder formulation than the emulsifiable concentrate formulation. ADI:0.011 mg/kg.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae: ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.31 mg/l.Bees:LD50(oral ) >104.4mg/bee; (contact) >200 mg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >10 000, mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) >1.8-7 mg/l.Fish:LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 2.2-2.7 mg/l.
Environmental fate:
Animals:The excretion of the parent compound and its biotransformation products is rapid, and occurs mainly via the faeces.Soil:Direct photodegradation in water contributes to overall degradation of bitertanol to only a low extent. Environmental DT50 in water is 1 mo to 1 y. Degradation in soil is rapid; CO2 is the most importPlant:The concentration of bitertanol in plant tissues is negligible. The active ingredient could be determined on the surface of fruits and leaves of treated plants. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
EU to withdraw approval of fungicide bitertanol
Related CompaniesMore
Jiangsu Sword Agrochemicals Co., Ltd.
Country: China
Triadimefon Triadimenol Tebuconazole Diniconazole Bitertanol Cyproconazole Propineb Paclobutrazol Metribuzin Bentazone
Country: India

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe