-
Common NameImibenconazole
-
中文通用名亚胺唑
-
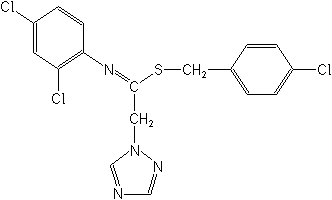
IUPAC4-chlorobenzyl (EZ)-N-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)thioacetamidate
-
CAS(4-chlorophenyl)methyl N-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanimidothioate
-
CAS No.86598-92-7
-
Molecular FormulaC17H13Cl3N4S
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityFungicide
Imibenconazole is a preventative and curative fungicide with high efficacy against scab in apple, pear and citrus and anthracnose in grapes. It is locally systemic with a high level of residual activity and rainfastness. The fungicide inhibits germ tube and mycelium growth. It can also inhibit spore germination of Elsinoe ampelina. Hokko recommends that fruit is sprayed at 14-day intervals and ornamentals at weekly intervals. Imibenconazole can be used either as a seed or foliar treatment on wheat. The product is not phytotoxic to target crops.
In field trials on apples, imibenconazole gave greater control of leaf and fruit infections than bitertanol. -
CropUseCropUses:
wheat, fruits, vines, peanuts, beans, tea, flowers, turf
vines
4-7.5 g ai/hl
top fruit
2.5-5 g ai/hl
ornamentals
7.5 g ai/hl
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:411.7; Physical form:Pale yellowish crystals. Melting point:89.5-90 °C; Vapour pressure:8.5 × 10-5 mPa (25 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 4.94; Solubility:In water 1.7 mg/l (20 °C). In acetone 1063, benzene 580, xylene 250, methanol 120 (all in g/l, 25 °C).; Stability:Stable in weak alkali; unstable in acid and in strong alkali; DT50 <1 d ( pH 1), 6 d ( pH 5), 88 d ( pH 7), 92 d ( pH 9), <1 d ( pH 13) (25 °C).
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2800, female rats 3000, male and female mice >5000 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Slight irritant to eyes; non-irritant to skin (rabbits). Slight skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >1020 mg/m3.
-
Environmental Profile
Ecotoxicology:
Algae: EC50 for algae >1000 mg/l.Bees: LD50 (oral) >125 μg/bee; (contact) >200 μg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 mg/ kg.Daphnia: LC50 (6 h) >100 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.0, rainbow trout 0.67, carp 0.84 mg/l.Worms: LC50 for earthworms >1000 mg/ kg soil.
Environmental fate:
Animals:Imibenconazole orally administered to rats is rapidly metabolised and eliminated. The major metabolite is 2',4'-dichloro-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)acetanilide.Soil:Rapidly degrades in soil: DT50 (lab.) 4-20 d, (field) 1-28 d. Koc 2813-23 391.Plant:Imibenconazole applied to grapes and apples is degraded or metabolised rapidly. The main metabolite is 2',4'-dichloro-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)acetanilide. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe